Immunoprotection of cellular transplants for autoimmune type 1 diabetes through local drug delivery
- PMID: 38286164
- PMCID: PMC11140763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2024.115179
Immunoprotection of cellular transplants for autoimmune type 1 diabetes through local drug delivery
Abstract
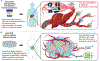
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is an autoimmune condition that results in the destruction of insulin-secreting β cells of the islets of Langerhans. Allogeneic islet transplantation could be a successful treatment for T1DM; however, it is limited by the need for effective, permanent immunosuppression to prevent graft rejection. Upon transplantation, islets are rejected through non-specific, alloantigen specific, and recurring autoimmune pathways. Immunosuppressive agents used for islet transplantation are generally successful in inhibiting alloantigen rejection, but they are suboptimal in hindering non-specific and autoimmune pathways. In this review, we summarize the challenges with cellular immunological rejection and therapeutics used for islet transplantation. We highlight agents that target these three immune rejection pathways and how to package them for controlled, local delivery via biomaterials. Exploring macro-, micro-, and nano-scale immunomodulatory biomaterial platforms, we summarize their advantages, challenges, and future directions. We hypothesize that understanding their key features will help identify effective platforms to prevent islet graft rejection. Outcomes can further be translated to other cellular therapies beyond T1DM.
Keywords: Allogeneic; Allograft; Autoimmunity; Biomaterials; Controlled release; Immune rejection; Immunosuppression; Islet transplantation.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Leslie RD, Evans-Molina C, Freund-Brown J, Buzzetti R, Dabelea D, Gillespie KM, Goland R, Jones AG, Kacher M, Phillips LS, Rolandsson O, Wardian JL, Dunne JL, Adult-onset type 1 diabetes: current understanding and challenges, Diabetes Care. 44 (2021) 2449–2456, 10.2337/dc21-0770. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bresson D, Von Herrath M, Mechanisms underlying type I diabetes, Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 1 (2004) 321–327, 10.1016/j.ddmec.2004.11.015. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

