Ribose-cysteine and levodopa abrogate Parkinsonism via the regulation of neurochemical and redox activities in alpha-synuclein transgenic Drosophila melanogaster models
- PMID: 38286464
- PMCID: PMC10826630
- DOI: 10.1080/19336934.2024.2306687
Ribose-cysteine and levodopa abrogate Parkinsonism via the regulation of neurochemical and redox activities in alpha-synuclein transgenic Drosophila melanogaster models
Abstract
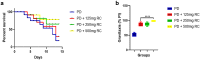
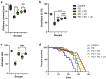
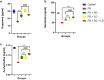
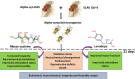
Parkinson's disease (PD), the most prevalent type of parkinsonism, is a progressive neurodegenerative condition marked by several non-motor and motor symptoms. PD is thought to have a complex aetiology that includes a combination of age, genetic predisposition, and environmental factors. Increased expression of α-synuclein (α-Syn) protein is central to the evolvement of neuropathology in this devastating disorder, but the potential of ribose-cysteine and levodopa in abating pathophysiologic changes in PD model is unknown. Crosses were set up between flies conditionally expressing a pathological variant of human α-Syn (UAS-α-Syn) and those expressing GAL4 in neurons (elav-GAL4) to generate offspring referred to as PD flies. Flies were randomly assigned to five groups (n = 40) from the total population of flies, with each group having five replicates. Groups of PD flies were treated with either 500 mg/kg ribose-cysteine diet, 250 mg/kg levodopa diet, or a combination of the two compounds for 21 days, whereas the control group (w1118) and the PD group were exposed to a diet without ribose-cysteine or levodopa. In addition to various biochemical and neurochemical assays, longevity, larval motility, and gravitaxis assays were carried out. Locomotive capability, lifespan, fecundity, antioxidant state, and neurotransmitter systems were all significantly (p < 0.05) compromised by overexpression of α-Syn. However, flies treated both ribose cysteine and levodopa showed an overall marked improvement in motor functions, lifespan, fecundity, antioxidant status, and neurotransmitter system functions. In conclusion, ribose-cysteine and levodopa, both singly and in combination, potentiated a therapeutic effect on alpha-synuclein transgenic Drosophila melanogaster models of Parkinsonism.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Drosophila melanogaster; Parkinsonism; levodopa; neurochemical; ribose-cysteine; transgenic.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Ishola I, Awogbindin IO, Olubodun-Obadun TG, et al. Vinpocetine prevents rotenone-induced Parkinson disease motor and non-motor symptoms through attenuation of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and α-synuclein expressions in rats. Neurotoxicology. 2023;96:37–52. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2023.03.002 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
