Regulation of ULK1 by WTAP/IGF2BP3 axis enhances mitophagy and progression in epithelial ovarian cancer
- PMID: 38286802
- PMCID: PMC10824720
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06477-0
Regulation of ULK1 by WTAP/IGF2BP3 axis enhances mitophagy and progression in epithelial ovarian cancer
Abstract
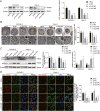
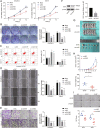
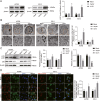
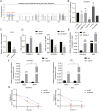
There is a pressing need for innovative therapeutic strategies for patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Previous studies have shown that UNC-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1), a serine/threonine kinase, is crucial in regulating cellular autophagy and mitophagy across various tumor types. However, the clinical implications, biological functions, and potential mechanisms of ULK1 in EOC remain poorly understood. This study demonstrates that ULK1 expression is upregulated in EOC tissue samples and EOC cell lines, with increased ULK1 expression correlating with poor prognosis. Functionally, overexpressed ULK1 enhances the proliferation and migration abilities of EOC cells both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ULK1 was identified as an m6A target of WTAP. WTAP-mediated m6A modification of ULK1 enhanced its mRNA stability in an IGF2BP3-dependent manner, leading to elevated ULK1 expression and enhanced mitophagy in EOC. In summary, our research reveals that the WTAP/IGF2BP3-ULK1 axis significantly influences protective mitophagy in EOC, contributing to its progression. Therefore, the regulatory mechanisms and biological function of ULK1 identify it as a potential molecular target for therapeutic intervention in EOC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

