Loss of Pip4k2c confers liver-metastatic organotropism through insulin-dependent PI3K-AKT pathway activation
- PMID: 38286827
- PMCID: PMC11175596
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-023-00704-x
Loss of Pip4k2c confers liver-metastatic organotropism through insulin-dependent PI3K-AKT pathway activation
Abstract
Liver metastasis (LM) confers poor survival and therapy resistance across cancer types, but the mechanisms of liver-metastatic organotropism remain unknown. Here, through in vivo CRISPR-Cas9 screens, we found that Pip4k2c loss conferred LM but had no impact on lung metastasis or primary tumor growth. Pip4k2c-deficient cells were hypersensitized to insulin-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling and exploited the insulin-rich liver milieu for organ-specific metastasis. We observed concordant changes in PIP4K2C expression and distinct metabolic changes in 3,511 patient melanomas, including primary tumors, LMs and lung metastases. We found that systemic PI3K inhibition exacerbated LM burden in mice injected with Pip4k2c-deficient cancer cells through host-mediated increase in hepatic insulin levels; however, this circuit could be broken by concurrent administration of an SGLT2 inhibitor or feeding of a ketogenic diet. Thus, this work demonstrates a rare example of metastatic organotropism through co-optation of physiological metabolic cues and proposes therapeutic avenues to counteract these mechanisms.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
B.I. has received consulting fees/honoraria from Volastra Therapeutics Inc, Merck, AstraZeneca, Eisai and Janssen Pharmaceuticals and has received research funding to Columbia University from Alkermes, Arcus Biosciences, Checkmate Pharmaceuticals, Compugen, Immunocore, and Synthekine. None of these are relevant to the current work. C.G. has received consulting fees from Watershed Informatics. S.F.B. owns equity in, receives compensation from, and serves as a consultant and the Scientific Advisory Board and Board of Directors of Volastra Therapeutics Inc. L.C.C. is a co-founder, member of the SAB, and holds equity in Agios, Petra, Volastra Therapeutics Inc., Faeth, and Larkspur. These companies are developing novel therapies for cancer, though drugs from these companies are not discussed in this manuscript. DS reports grants (to institution) from Amgen, Array/Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Novartis, and Roche; consulting fees/honoraria from 4SC, Amgen, Array Biopharma, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Haystick, Immunocore, InFlarX, Innocent, LabCorp, Merck Serono, MSD, Nektar, NeraCare, Novartis, OncoSec, Pfizer, Philogen, Pierre Fabre, Replimune, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi/Regeneron, and Sun Pharma; support for attendings meetings or travel support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, and Sanofi; participation on drug safety monitoring or advisory boards for 4SC, Amgen, Array Biopharma, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Immunocore, InFlarX, Merck Serono, MSD, Nektar, NeraCare, Novartis, OncoSec, Pfizer, Philogen, Pierre Fabre, Replimune, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi/Regeneron, and SunPharma; and leadership roles for DeCOG, German Cancer Society, Hiege-Stiftung, Deutsche Hautkrebsstiftung, Nationale Versorgungskonferenz Hautkrebs (NVKH) and European Melanoma Registry (EuMelaReg). S.K.D., S.W. and G.S. are employees of Caris Life Sciences. The remaining authors declare no competing interests
Figures
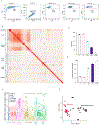
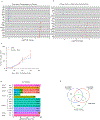



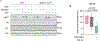






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 CA258829/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA280414/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA280572/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007367/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD026395/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD032433/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA256188/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA274506/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K00 CA234950/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK119886/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA266446/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM132083/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD030544/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA281104/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

