Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
- PMID: 38286997
- PMCID: PMC10824767
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45144-y
Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
Abstract
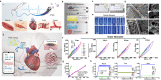
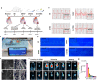
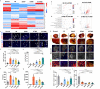
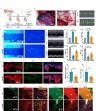
During myocardial infarction, microcirculation disturbance in the ischemic area can cause necrosis and formation of fibrotic tissue, potentially leading to malignant arrhythmia and myocardial remodeling. Here, we report a microchanneled hydrogel suture for two-way signal communication, pumping drugs on demand, and cardiac repair. After myocardial infarction, our hydrogel suture monitors abnormal electrocardiogram through the mobile device and triggers nitric oxide on demand via the hydrogel sutures' microchannels, thereby inhibiting inflammation, promoting microvascular remodeling, and improving the left ventricular ejection fraction in rats and minipigs by more than 60% and 50%, respectively. This work proposes a suture for bidirectional communication that acts as a cardio-patch to repair myocardial infarction, that remotely monitors the heart, and can deliver drugs on demand.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lee, D. S. et al. Prospective validation of the emergency heart failure mortality risk grad for acute heart failure: the acute congestive heart failure urgent care evaluation (ACUTE) study. Circulation.139, 1146–1156 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

