RNA polymerase II pausing is essential during spermatogenesis for appropriate gene expression and completion of meiosis
- PMID: 38287033
- PMCID: PMC10824759
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45177-3
RNA polymerase II pausing is essential during spermatogenesis for appropriate gene expression and completion of meiosis
Abstract
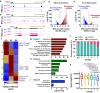
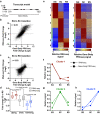
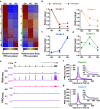
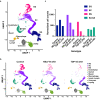
Male germ cell development requires precise regulation of gene activity in a cell-type and stage-specific manner, with perturbations in gene expression during spermatogenesis associated with infertility. Here, we use steady-state, nascent and single-cell RNA sequencing strategies to comprehensively characterize gene expression across male germ cell populations, to dissect the mechanisms of gene control and provide new insights towards therapy. We discover a requirement for pausing of RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) at the earliest stages of sperm differentiation to establish the landscape of gene activity across development. Accordingly, genetic knockout of the Pol II pause-inducing factor NELF in immature germ cells blocks differentiation to spermatids. Further, we uncover unanticipated roles for Pol II pausing in the regulation of meiosis during spermatogenesis, with the presence of paused Pol II associated with double-strand break (DSB) formation, and disruption of meiotic gene expression and DSB repair in germ cells lacking NELF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.A. received research funding from Novartis not related to this work, is a consultant for Odyssey Therapeutics, and is on the SAB of CAMP4 Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
RNA polymerase II pausing is essential during spermatogenesis for appropriate gene expression and completion of meiosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 9:2023.05.08.539879. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.08.539879. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 29;15(1):848. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45177-3. PMID: 37215034 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

