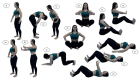Can 5-weeks of Hypopressive Exercise Influence Sagittal Lumbo-Pelvic Position in Athletic and Non-Athletic Females?
- PMID: 38288077
- PMCID: PMC10824316
- DOI: 10.70252/KHQG8688
Can 5-weeks of Hypopressive Exercise Influence Sagittal Lumbo-Pelvic Position in Athletic and Non-Athletic Females?
Abstract
Hypopressive exercises (HE) are part of the Low Pressure Fitness training program which is widely used by physical therapists in the rehabilitation of the pelvic floor, abdominal and spinal musculature. The aim of this study was to compare the effects of HE on the sagittal lumbo-pelvic posture in athletic and non-athletic females. It was hypothesized that a 5-week training program of HE could influence lumbo-pelvic position while reducing abdominal circumference and low back pain in athletic and non-athletic females. Twenty normoweight females (mean age = 24.8 (SD 3.5) years; body mass index = 22.4 (SD 1.6) kg/m2) participated in this study. Ten athletic females were rugby players (RG), and 10 females were non-athletic (SG). Participants completed twenty minutes of HE twice weekly for 5 weeks. Before and after the intervention, two-dimension photogrammetry was used to assess lumbar lordosis and pelvic horizontal alignment. A Visual Analog Scale was used to assess low back pain and cirtometry was used to assess abdominal circumferences at umbilical, supra and infra-umbilical levels. An analysis of variance between moments revealed no significant differences in lumbar lordosis and pelvic positioning but showed significant differences for abdominal circumferences between groups. No significant differences between groups were found for other variables. Significant correlations were found between the three different abdominal circumference measurements (p > 0.05) but not between lumbar lordosis and abdominal circumferences. These preliminary findings indicate that a 5-week HE intervention displayed non-significant changes in lumbar lordosis, pelvic horizontal alignment, and low back pain but a significant reduction in abdominal circumferences in non-athletic and athletic females.
Keywords: Sagittal alignment; abdominal circumference; breathing exercise; low back pain; lumbar lordosis; pelvic tilt.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Hypopressive Exercise on Posterior Back Chain Kinematics and Pulmonary Function in Professional Female Basketball Players.J Sport Rehabil. 2022 Mar 1;31(3):305-312. doi: 10.1123/jsr.2021-0025. Epub 2021 Dec 20. J Sport Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 34929664
-
How consistent are lordosis, range of movement and lumbo-pelvic rhythm in people with and without back pain?BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Sep 22;17(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1250-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 27658946 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Abdominal Obesity and Sagittal Imbalance on Sacroiliac Joint Pain After Lumbar Fusion.Pain Physician. 2024 Jan;27(1):59-67. Pain Physician. 2024. PMID: 38285036
-
Relationships between forward head posture and lumbopelvic sagittal alignment in older adults with chronic low back pain.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021 Oct;28:150-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2021.07.036. Epub 2021 Aug 8. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021. PMID: 34776134
-
Spinopelvic Parameters: Lumbar Lordosis, Pelvic Incidence, Pelvic Tilt, and Sacral Slope: What Does a Spine Surgeon Need to Know to Plan a Lumbar Deformity Correction?Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2018 Jul;29(3):323-329. doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2018.03.003. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2018. PMID: 29933800 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Hypopressive Abdominal Training on Ventilatory Capacity and Quality of Life: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;12(9):893. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12090893. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38727450 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Hypopressive Exercise on Dynamic Neuromuscular Control in Female Roller-Skaters.Int J Exerc Sci. 2024 Jan 1;17(6):252-264. doi: 10.70252/PTIM9626. eCollection 2024. Int J Exerc Sci. 2024. PMID: 38665680 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Body Posture Assessed by Dynamic Baropodometry and Dental Occlusion in Patients with and without Dental Pathology.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 17;24(6):1921. doi: 10.3390/s24061921. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38544184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abelin-Genevois K. Sagittal balance of the spine. Orthop Traumatol Surg & Res. 2021;107(1S):102769. - PubMed
-
- Álvarez Sáez MM, Rial Rebullido T, Chulvi Medrano I, García Soidán JL, Cortell Tormo JM. ¿Puede un programa de ocho semanas basado en técnicas hipopresivas producir cambios en la función del suelo pélvico y composición corporal de jugadoras de rugby? [Can an eight-week program based on the hypopressive technique produce changes in pelvic floor]. Retos. 2016;30:26–29.
-
- Araújo F, Lucas R, Alegrete N, Azevedo A, Barros H. Individual and contextual characteristics as determinants of sagittal standing posture: A population-based study of adults. Spine J. 2014;14(10):2373–2383. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal SK, Misra A, Aggarwal P, Bardia A, Goel R, Vikram NK, Wasir JS, Hussain N, Ramachandran K, Pandey RM. Waist circumference measurement by site, posture, respiratory phase, and meal time: Implications for methodology. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009;17(5):1056–1061. - PubMed
-
- Baroni BM, Bruscatto CA, Rech RR, Trentin L, Brum LR. Prevalência de alterações posturais em praticantes de musculação. Fisioter Mov. 2010;23(1):129–139.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources