Exploring the untapped pharmacological potential of imidazopyridazines
- PMID: 38288152
- PMCID: PMC10823362
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra07280k
Exploring the untapped pharmacological potential of imidazopyridazines
Abstract
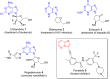
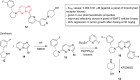
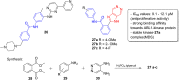
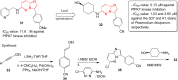
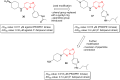
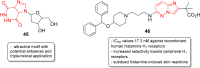
Imidazopyridazines are fused heterocycles, like purines, with a pyridazine ring replacing the pyrimidine ring in purines. Imidazopyridazines have been primarily studied for their kinase inhibition activity in the development of new anticancer and antimalarial agents. In addition to this, they have also been investigated for their anticonvulsant, antiallergic, antihistamine, antiviral, and antitubercular properties. Herein, we review the background and development of different imidazopyridazines as potential pharmacological agents. Moreover, the scope of this relatively less charted heterocyclic scaffold is also highlighted.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

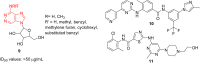







References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

