Vitamin D-mediated tsRNA-07804 triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and suppresses non-small cell lung cancer progression by targeting CRKL
- PMID: 38289488
- PMCID: PMC10827823
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05586-1
Vitamin D-mediated tsRNA-07804 triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and suppresses non-small cell lung cancer progression by targeting CRKL
Abstract
Objective: tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) are novel non-coding RNAs with various functions in multiple cancers. Nevertheless, whether vitamin D executes its function in mitochondrial dysfunction and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression through tsRNAs remains obscure.
Methods: Differentially expressed tsRNAs between control and vitamin D-treated H1299 cells were acquired by small RNA sequencing. Cell and animal experiments were implemented to elucidate the impacts of vitamin D and tsRNA on mitochondrial dysfunction and NSCLC progression. Dual-luciferase reporter assay, quantitative real-time PCR, western blot and recovery experiments were applied to determine the mechanism of tsRNA in NSCLC.
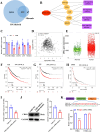
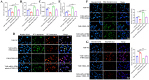
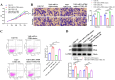
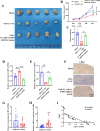
Results: We discovered that vitamin D receptor resulted in decreased mitochondrial-related functions and vitamin D caused mitochondrial dysfunction of NSCLC cells. tsRNA-07804 was remarkably upregulated in vitamin D-treated H1299 cells. Functional experiments indicated that vitamin D led to mitochondrial dysfunction, repressed the proliferation, migration, invasion, and promoted apoptosis of H1299 cells via regulating tsRNA-07804. Mechanistically, tsRNA-07804 induced mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibited the malignancy of H1299 cells by suppressing CRKL expression. In vivo experiments showed that vitamin D inhibited the tumor growth in NSCLC by increasing tsRNA-07804 expression. Moreover, clinical sample analysis unveiled that tsRNA-07804 had a negative correlation with CRKL.
Conclusions: In conclusion, our study proved that vitamin D induced mitochondrial dysfunction and suppressed the progression of NSCLC through the tsRNA-07804/CRKL axis. Overall, these results unveiled that tsRNA-07804 might act as a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC.
Keywords: CRKL; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Non-small cell lung cancer; Progression; Vitamin D; tsRNA-07804.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research progress on the tsRNA biogenesis, function, and application in lung cancer.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Sep 4;10:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.09.004. eCollection 2025 Feb. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39309197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TsRNA-49-73-Glu-CTC: A promising serum biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 28;20(3):e0320187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320187. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40153423 Free PMC article.
-
A novel cytostatic form of autophagy in sensitization of non-small cell lung cancer cells to radiation by vitamin D and the vitamin D analog, EB 1089.Autophagy. 2014;10(12):2346-61. doi: 10.4161/15548627.2014.993283. Autophagy. 2014. PMID: 25629933 Free PMC article.
-
SNHG14 silencing suppresses the progression and promotes cisplatin sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109164. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109164. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31252267
-
Unveiling the role of tRNA-derived small RNAs in MAPK signaling pathway: implications for cancer and beyond.Front Genet. 2024 Mar 26;15:1346852. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1346852. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38596214 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Indispensable Roles of GMDS and GMDS-AS1 in the Advancement of Cancer: Fucosylation, Signal Pathway and Molecular Pathogenesis.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(19):1712-1722. doi: 10.2174/0113895575285276240324080234. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38591197 Review.
-
Transfer RNA‑derived small RNAs: A class of potential biomarkers in multiple cancers (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 May 1;28(1):293. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14427. eCollection 2024 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38737976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the tsRNA biogenesis, function, and application in lung cancer.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Sep 4;10:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.09.004. eCollection 2025 Feb. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39309197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: A Synergistic Approach to Enhancing Treatment Efficacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 9;26(10):4511. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104511. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carlberg C, Munoz A (2022) An update on vitamin D signaling and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 79:217–230. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.05.018 - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Katz LH, Munoz NM, Gu S, Shin JH, Jogunoori WS, Lee MH, Belkin MD, Kim SB, White JC, Andricovich J, Tzatsos A, Li S, Kim SS, Shetty K, Mishra B, Rashid A, Lee JS, Mishra L (2016) Vitamin D deficiency promotes liver tumor growth in transforming growth factor-beta/Smad3-deficient mice through wnt and toll-like receptor 7 pathway modulation. Sci Rep 6:30217. 10.1038/srep30217 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

