Burden of osteoarthritis in China, 1990-2019: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
- PMID: 38289570
- PMCID: PMC10876716
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-024-06885-9
Burden of osteoarthritis in China, 1990-2019: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
Abstract
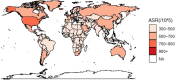
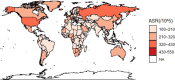
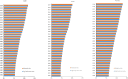
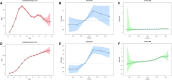
This study aimed to report the most current data on the incidence and disability-adjusted life years (DALY) associated with osteoarthritis in China from 1990 to 2019. Publicly available modelled data from Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) 2019 were used. The incidence and DALY, due to osteoarthritis in China, stratified by sex, trends of associated risk factors, assess the age, period, and cohort effects on the long-term trends of osteoarthritis incidence and DALY in China from 1990 to 2019. We found that the age-standardized incidence and DALY rates of osteoarthritis in China are higher than the average levels in Asia, Africa, and Oceania. In 2019, the number of cases of osteoarthritis in China was 10,681,311, an increase of 132.66% compared with 1990. the DALY of osteoarthritis in China was 4,724,885 person-years, which was 159.70% higher than that in 1990. In 2019, the incidence and DALY rates of osteoarthritis in China was 750.96/100,000,332.19/100,000. High body-mass as risk factors for osteoarthritis DALY with the population attributable proportion (PAF) increasing steadily from 1990 to 2019. The incidence and DALY rates of three types of osteoarthritis from high to low are osteoarthritis knee, osteoarthritis hand, and osteoarthritis hip. Age-period-cohort model showed that the incidence rate of osteoarthritis in China shows a trend of increasing first and then decreasing with age; concurrently, the DALY rate of osteoarthritis in China increased with age. For the period effect, we found that the period rate ratio (RR) of osteoarthritis incidence and DALY rates kept increasing in the cohort born before 2005-2009, and then, it was gradually reduced by year of birth in the cohort born after 2005-2009. As for cohort effect, the cohort RR of incidence rate of osteoarthritis almost has no change, while the cohort RR of DALY rate of osteoarthritis kept increasing from 1990 to 2019. The burden and impact of osteoarthritis in China are substantial and are increasing. Adopting suitable control and preventive community measures to reduce modifiable risk factors is needed to reduce the current and future burden of osteoarthritis in China. Key Points • This paper analyzes the disease burden of osteoarthritis in China for the first time and discusses the influence on the disease burden of osteoarthritis from the perspectives of age, period, and cohort.
Keywords: China; Disability-adjusted life years; Incidence; Osteoarthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Petersen KK, Drewes AM, Olesen AE, Ammitzbøll N, Bertoli D, Brock C, et al. The effect of duloxetine on mechanistic pain profiles, cognitive factors and clinical pain in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis-a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Eur J Pain. 2022;26(8):1650–1664. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

