Texture-Based Radiomic SD-OCT Features Associated With Response to Anti-VEGF Therapy in a Phase III Neovascular AMD Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38289610
- PMCID: PMC10833054
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.13.1.29
Texture-Based Radiomic SD-OCT Features Associated With Response to Anti-VEGF Therapy in a Phase III Neovascular AMD Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: The goal of this study was to evaluate the role of texture-based baseline radiomic features (Fr) and dynamic radiomics alterations (delta, FΔr) within multiple targeted compartments on optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans to predict response to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD).
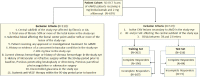
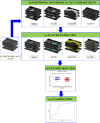
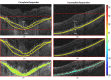
Methods: HAWK is a phase 3 clinical trial data set of active nAMD patients (N = 1082) comparing brolucizumab and aflibercept. This analysis included patients receiving 6 mg brolucizumab or 2 mg aflibercept and categorized as complete responders (n = 280) and incomplete responders (n = 239) based on whether or not the eyes achieved/maintained fluid resolution on OCT. A total of 481 Fr were extracted from each of the fluid, subretinal hyperreflective material (SHRM), retinal tissue, and sub-retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) compartments. Most discriminating eight baseline features, selected by the minimum redundancy, maximum relevance feature selection, were evaluated using a quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) classifier on the training set (Str, n = 363) to differentiate between the two patient groups. Classifier performance was subsequently validated on independent test set (St, n = 156).
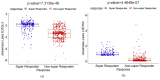
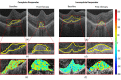
Results: In total, 519 participants were included in this analysis from the HAWK phase 3 study. There were 280 complete responders and 219 incomplete responders. Compartmental analysis of radiomics featured identified the sub-RPE and SHRM compartments as the most distinguishing between the two response groups. The QDA classifier yielded areas under the curve of 0.78, 0.79, and 0.84, respectively, using Fr, FΔr, and combined Fr, FΔr, and Fc on St.
Conclusions: Utilizing compartmental static and dynamic radiomics features, unique differences were identified between eyes that respond differently to anti-VEGF therapy in a large phase 3 trial that may provide important predictive value.
Translational relevance: Imaging biomarkers, such as radiomics features identified in this analysis, for predicting treatment response are needed to enhanced precision medicine in the management of nAMD.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
Similar articles
-
OCT-Derived Radiomic Features Predict Anti-VEGF Response and Durability in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Ophthalmol Sci. 2022 May 18;2(4):100171. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2022.100171. eCollection 2022 Dec. Ophthalmol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36531588 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Assessment of Ellipsoid Zone Integrity, Subretinal Hyperreflective Material, and Subretinal Pigment Epithelium Disease in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Ophthalmol Retina. 2021 Dec;5(12):1204-1213. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Ophthalmol Retina. 2021. PMID: 33640493 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multi-Compartment Spatially-Derived Radiomics From Optical Coherence Tomography Predict Anti-VEGF Treatment Durability in Macular Edema Secondary to Retinal Vascular Disease: Preliminary Findings.IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2021 Jul 12;9:1000113. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2021.3096378. eCollection 2021. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2021. PMID: 34350068 Free PMC article.
-
Brolucizumab: Evolution through Preclinical and Clinical Studies and the Implications for the Management of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Ophthalmology. 2020 Jul;127(7):963-976. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.12.031. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Ophthalmology. 2020. PMID: 32107066 Review.
-
Non-ICGA treatment criteria for Suboptimal Anti-VEGF Response for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy: APOIS PCV Workgroup Report 2.Ophthalmol Retina. 2021 Oct;5(10):945-953. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2021.04.002. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Ophthalmol Retina. 2021. PMID: 33866022
Cited by
-
Radiomics-Based OCT Analysis of Choroid Reveals Biomarkers of Central Serous Chorioretinopathy.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025 Apr 1;14(4):23. doi: 10.1167/tvst.14.4.23. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40266602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh SR, Lupidi M, Mishra SB, Paez-Escamilla M, Querques G, Chhablani J. Unique optical coherence tomographic features in age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 2020; 65(4): 451–457. - PubMed
-
- Rashno A, Koozekanani DD, Drayna PM, et al. . Fully automated segmentation of fluid/cyst regions in optical coherence tomography images with diabetic macular edema using neutrosophic sets and graph algorithms. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2018; 65(5): 989–1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA216579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR012463/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY025585/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA239055/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA268287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA249992/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA202752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA208236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA248226/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004121/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R43 EB028736/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA269181/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA257612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA254566/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA220581/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 EY022947/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

