Pharmacological modulation of RB1 activity mitigates resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer
- PMID: 38289962
- PMCID: PMC10861914
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2304619121
Pharmacological modulation of RB1 activity mitigates resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer
Abstract
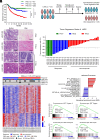
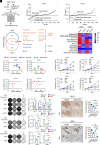
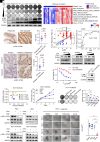
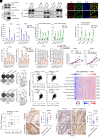
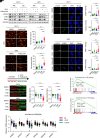
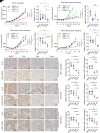
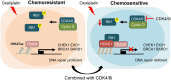
Resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy leads to poor prognosis of locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC), representing an unmet clinical need that demands further exploration of therapeutic strategies to improve clinical outcomes. Here, we identified a noncanonical role of RB1 for modulating chromatin activity that contributes to oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer (CRC). We demonstrate that oxaliplatin induces RB1 phosphorylation, which is associated with the resistance to neoadjuvant oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in LARC. Inhibition of RB1 phosphorylation by CDK4/6 inhibitor results in vulnerability to oxaliplatin in both intrinsic and acquired chemoresistant CRC. Mechanistically, we show that RB1 modulates chromatin activity through the TEAD4/HDAC1 complex to epigenetically suppress the expression of DNA repair genes. Antagonizing RB1 phosphorylation through CDK4/6 inhibition enforces RB1/TEAD4/HDAC1 repressor activity, leading to DNA repair defects, thus sensitizing oxaliplatin treatment in LARC. Our study identifies a RB1 function in regulating chromatin activity through TEAD4/HDAC1. It also provides the combination of CDK4/6 inhibitor with oxaliplatin as a potential synthetic lethality strategy to mitigate oxaliplatin resistance in LARC, whereby phosphorylated RB1/TEAD4 can serve as potential biomarkers to guide the patient stratification.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitor; drug resistance; locally advanced rectal cancer; neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effects of oxaliplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy and chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: a single-center, retrospective cohort study.World J Surg Oncol. 2018 Jun 5;16(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1403-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29871650 Free PMC article.
-
Individual tumor volume responses to short-course oxaliplatin-containing induction chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer - Targeting the tumor for radiation sensitivity?Radiother Oncol. 2016 Jun;119(3):505-11. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.02.020. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Radiother Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26968754
-
[Analysis on efficacy and safety of total neoadjuvant therapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer with high risk factors].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 25;22(4):349-356. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2019.04.007. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31054549 Chinese.
-
The Evolving Neoadjuvant Treatment Paradigm for Patients with Locoregional mismatch Repair Proficient Rectal Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022 Apr;23(4):453-473. doi: 10.1007/s11864-022-00961-5. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35312962 Review.
-
Implications of recent neoadjuvant clinical trials on the future practice of radiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Feb 14;29(6):1011-1025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1011. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36844136 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the ZMYM2-ANXA9 Axis with FLT3 Inhibitor G749 Overcomes Oxaliplatin Resistance in Colorectal Cancer.Biomedicines. 2025 May 20;13(5):1247. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051247. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427072 Free PMC article.
-
Ligustrazine nano-drug delivery system ameliorates doxorubicin-mediated myocardial injury via piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1-prohibitin 2-mediated mitochondrial quality surveillance.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 27;23(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03420-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40426179 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC-driven mechanisms in anticancer resistance: epigenetics and beyond.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Nov 20;7:46. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.103. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39624079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Untangling the Role of MYC in Sarcomas and Its Potential as a Promising Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 25;26(5):1973. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051973. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4'-Demethylpodophyllotoxin functions as a mechanism-driven therapy by targeting the PI3K-AKT pathway in Colorectal cancer.Transl Oncol. 2025 Jan;51:102199. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102199. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39631206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F., et al. , Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394–424 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Body A., et al. , Neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: Recent advances and ongoing challenges. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 20, 29–41 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

