Clinical utility of Next Generation Sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA for the molecular profiling of patients with NSCLC at diagnosis and disease progression
- PMID: 38290249
- PMCID: PMC10859238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101869
Clinical utility of Next Generation Sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA for the molecular profiling of patients with NSCLC at diagnosis and disease progression
Abstract
Background: The present study evaluates the utility of NGS analysis of circulating free DNA (cfDNA), which incorporates small amounts of tumor DNA (ctDNA), at diagnosis or at disease progression (PD) in NSCLC patients.
Methods: Comprehensive genomic profiling on cfDNA by NGS were performed in NSCLC patients at diagnosis (if tissue was unavailable/insufficient) or at PD to investigate potential druggable molecular aberrations. Blood samples were collected as routinary diagnostic procedures, DNA was extracted, and the NextSeq 550 Illumina platform was used to run the Roche Avenio ctDNA Expanded Kit for molecular analyses. Gene variants were classified accordingly to the ESCAT score.
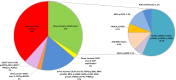
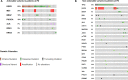
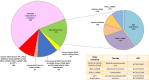
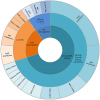
Results: A total of 106 patients were included in this study; 44 % of cases were requested because of tissue unavailability at the diagnosis and 56 % were requested at the PD. At least one driver alteration was observed in 62 % of cases at diagnosis. Driver druggable variants classified as ESCAT level I were detected in 34 % of patients, including ALK-EML4, ROS1-CD74, EGFR, BRAF, KRAS p.G12C, PI3KCA. In the PD group, most patients were EGFR-positive, progressing to a first line-therapy. Sixty-three percent of patients had at least one driver alteration detected in blood and 17 % of patients had a known biological mechanism of resistance allowing further therapeutic decisions.
Conclusions: The present study confirms the potential of liquid biopsy to detect tumour molecular heterogeneity in NSCLC patients at the diagnosis and at PD, demonstrating that a significant number of druggable mutations and mechanisms of resistance can be detected by NGS analysis on ctDNA.
Keywords: Liquid biopsy; NGS; NSCLC; Predictive biomarkers; Resistance to treatment.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comprehensive molecular analysis of driver mutations in non-small cell lung carcinomas and its correlation with PD-L1 expression, An Indian perspective.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Jan;253:155013. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.155013. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38096714
-
Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Based on Circulating Cell-Free DNA and Impact of Variation Allele Frequency.Clin Lung Cancer. 2021 Jul;22(4):e519-e527. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.11.007. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33414052
-
Identification and monitoring of somatic mutations in circulating cell-free tumor DNA in lung cancer patients.Lung Cancer. 2019 Aug;134:225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.06.010. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31319985
-
Using circulating cell-free DNA to monitor personalized cancer therapy.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2017 May;54(3):205-218. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2017.1299683. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2017. PMID: 28393575 Review.
-
Understanding the Mechanisms of Resistance in EGFR-Positive NSCLC: From Tissue to Liquid Biopsy to Guide Treatment Strategy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 14;20(16):3951. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163951. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31416192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of actionable mutations in circulating tumor DNA for non-small cell lung cancer patients.Commun Med (Lond). 2025 May 28;5(1):204. doi: 10.1038/s43856-025-00921-8. Commun Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40437208 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation sequencing impact on cancer care: applications, challenges, and future directions.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 9;15:1420190. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1420190. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39045325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive liquid biopsy analysis for monitoring NSCLC patients under second-line osimertinib treatment.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 21;14:1435537. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1435537. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39497713 Free PMC article.
-
Association of mutation profiles with metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 11;14:1451576. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1451576. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39464712 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting actionable mutations from matched plasma-based versus tissue next-generation sequencing in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective single centre analysis on site.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 6;44(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03480-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40765058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hendriks L.E., Kerr K.M., Menis J., Mok T.S., Nestle U., Passaro A., et al. Oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023;34(4):339–357. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

