Low circulatory levels of total cholesterol, HDL-C and LDL-C are associated with death of patients with sepsis and critical illness: systematic review, meta-analysis, and perspective of observational studies
- PMID: 38290288
- PMCID: PMC10844818
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.104981
Low circulatory levels of total cholesterol, HDL-C and LDL-C are associated with death of patients with sepsis and critical illness: systematic review, meta-analysis, and perspective of observational studies
Abstract
Background: Mechanistic studies have established a biological role of sterol metabolism in infection and immunity with clinical data linking deranged cholesterol metabolism during sepsis with poorer outcomes. In this systematic review we assess the relationship between biomarkers of cholesterol homeostasis and mortality in critical illness.
Methods: We identified articles by searching a total of seven electronic databases from inception to October 2023. Prospective observational cohort studies included those subjects who had systemic cholesterol (Total Cholesterol (TC), HDL-C or LDL-C) levels assessed on the first day of ICU admission and short-term mortality recorded. Meta-analysis and meta-regression were used to evaluate overall mean differences in serum cholesterol levels between survivors and non-survivors. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale.
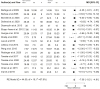
Findings: From 6469 studies identified by searches, 24 studies with 2542 participants were included in meta-analysis. Non-survivors had distinctly lower HDL-C at ICU admission -7.06 mg/dL (95% CI -9.21 to -4.91, p < 0.0001) in comparison with survivors. Corresponding differences were also seen less robustly for TC -21.86 mg/dL (95% CI -31.23 to -12.49, p < 0.0001) and LDL-C -8.79 mg/dL (95% CI, -13.74 to -3.83, p = 0.0005).
Interpretation: Systemic cholesterol levels (TC, HDL-C and LDL-C) on admission to critical care are inversely related to mortality. This finding is consistent with the notion that inflammatory and metabolic setpoints are coupled, such that the maladaptive-setpoint changes of cholesterol in critical illness are related to underlying inflammatory processes. We highlight the potential of HDL-biomarkers as early predictors of severity of illness and emphasise that future research should consider the metabolic and functional heterogeneity of HDLs.
Funding: EU-ERDF-Welsh Government Ser Cymru programme, BBSRC, and EU-FP7 ClouDx-i project (PG).
Keywords: Cholesterol; Critical illness; Immunometabolism; Lipids; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Peter Ghazal is a member of the development board for Sepsis Trust UK with no cash incentive, Received funding from the EDRF Ser Cymru (Welsh Government) programme, EU-FP7 projects: ClouDx-I and NeoVanc. Thorsten Förster is an inventor of patent US20170022568—“Molecular Predictors Of Sepsis” and is declared as an existing interest in intellectual property around transcriptomic markers of sepsis, but is not related to the current work beyond the broad theme of sepsis.
Figures




References
-
- Montecucco F., Favari E., Norata G.D., Ronda N., Nofer J.R., Vuilleumier N. Impact of systemic inflammation and autoimmune diseases on apoA-I and HDL plasma levels and functions. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2015;224:455–482. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25522998/ [cited 2023 Nov 19];Available from: - PubMed
-
- Kim S.Y., Yu M., Morin E.E., Kang J., Kaplan M.J., Schwendeman A. High-density lipoprotein in lupus: disease biomarkers and potential therapeutic strategy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(1):20–30. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31350818/ [cited 2023 Jun 19];Available from: - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim J.Y., Lee E.Y., Park J.K., Song Y.W., Kim J.R., Cho K.H. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis show altered lipoprotein profiles with dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins that can exacerbate inflammatory and atherogenic process. PLoS One. 2016;11(10) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27736980/ [cited 2023 Jun 19];Available from: - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robertson K.A., Ghazal P. Interferon control of the sterol metabolic network: bidirectional molecular circuitry-mediating host protection. Front Immunol. 2016;7:634. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28066443/ [cited 2023 Mar 14];Available from: - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

