Transmembrane protein TMEM97 and epigenetic reader BAHCC1 constitute an axis that supports pro-inflammatory cytokine expression
- PMID: 38290642
- PMCID: PMC10997414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111069
Transmembrane protein TMEM97 and epigenetic reader BAHCC1 constitute an axis that supports pro-inflammatory cytokine expression
Abstract
Pro-inflammatory cytokine production by the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a key etiology in retinal degenerative diseases, yet the underlying mechanisms are not well understood. TMEM97 is a scarcely studied transmembrane protein recently implicated in retinal degeneration. BAH domain coiled coil 1 (BAHCC1) is a newly discovered histone code reader involved in oncogenesis. A role for TMEM97 and BAHCC1 in RPE inflammation was not known. Here we found that they constitute a novel axis regulating pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in RPE cells. Transcriptomic analysis using a TMEM97-/- ARPE19 human cell line and the validation via TMEM97 loss- and gain-of-function revealed a profound role of TMEM97 in promoting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, notably IL1β and CCL2, and unexpectedly BAHCC1 as well. Moreover, co-immunoprecipitation indicated an association between the TMEM97 and BAHCC1 proteins. While TMEM97 ablation decreased and its overexpression increased NFκB (p50, p52, p65), the master transcription factor for pro-inflammatory cytokines, silencing BAHCC1 down-regulated NFκB and downstream pro-inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, in an RPE-damage retinal degeneration mouse model, immunofluorescence illustrated down-regulation of IL1β and CCL2 total proteins and suppression of glial activation in the retina of Tmem97-/- mice compared to Tmem97+/+ mice. Thus, TMEM97 is a novel determinant of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression acting via a previously unknown TMEM97- > BAHCC1- > NFκB cascade. SYNOPSIS: Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) inflammation can lead to blindness. We identify here a previously uncharacterized cascade that underlies RPE cell production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Specifically, transmembrane protein TMEM97 positively regulates the recently discovered histone code reader BAHCC1, which in turn enhances pro-inflammatory cytokine expression via the transcription factor NFκB.
Keywords: BAHCC1; NFκB; Pro-inflammatory cytokines; Retinal pigment epithelial cell; TMEM97.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have declared no competing interests and no industry or financial relationship to disclose.
Figures


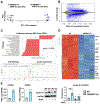
Data clustering. Triplicate WT cultures are labeled as CK1, CK2, and CK3. Triplicate KO cultures are labeled as of S2R1, S2R2, and S2R3.
MA plot showing distribution of differentially expressed genes.
Pathway analysis of the RNA-seq data. Top 20 identified KEGG pathways including the 4 upregulated and 16 downregulated are presented. GSEA: Gene set enrichment analysis. NES, normalized enrichment score.
Heatmap. Presented are the down-regulated genes that are included in the top 100 differentially expressed genes with highest q values (Padj, adjusted p value). Inflammation-associated genes are labeled on the right side of the heatmap.
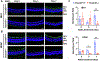
Western blot validation of cyclin D1 (CCND1) expression. TMEM97 WT and KO ARPE19 cells were incubated without or with 5 mM NaIO3 for 24h prior to cell collection for immunoblotting. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent repeat experiments). Statistics: One-way ANOVA/Tukey test; ***P<0.001. The RNA-seq data are FPKM values.

RNA-seq data indicating down-regulation of pro-inflammatory genes in TMEM97 KO cells. Data are presented as FPKM values. Each bar represents mean ± SEM of triplicate samples used for RNA-seq.
Effect of TMEM97 loss and gain of function on the mRNA levels of NFκB genes and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Effect of TMEM97 loss and gain of function on the protein levels of NFκB family members and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
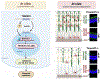
Schematic depiction of the proposed TMEM97-> NFκB-> cytokines cascade.

TMEM97 KO and OE markedly reduces and elevates BAHCC1 levels, respectively. RNA-seq data are presented as FPKM values (mean ± SEM).
BAHCC1 silencing down-regulates NFκB mRNA and protein levels.
BAHCC1 silencing down-regulates mRNA and protein levels or pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of BAHCC1 with TMEM97. Control (empty vector) and TMEM97 OE cell lines were cultured. IP was performed with an antibody against endogenous TMEM97 or non-specific IgG for control. Shown on the blot are 3 separate repeat experiments. GAPDH was detected with input samples.
References
-
- Holtkamp GM, Kijlstra A, Peek R and de Vos AF. Retinal pigment epithelium-immune system interactions: cytokine production and cytokine-induced changes. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001;20:29–48. - PubMed
-
- Nazari H, Zhang L, Zhu D, Chader GJ, Falabella P, Stefanini F, Rowland T, Clegg DO, Kashani AH, Hinton DR and Humayun MS. Stem cell based therapies for age-related macular degeneration: The promises and the challenges. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015;48:1–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

