Heterogeneity in disease activity, frequency of treatments, and visual outcomes among patients with retinal vein occlusion: relationship between injection need and vision with as-needed ranibizumab
- PMID: 38290802
- PMCID: PMC11347224
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo-2022-323120
Heterogeneity in disease activity, frequency of treatments, and visual outcomes among patients with retinal vein occlusion: relationship between injection need and vision with as-needed ranibizumab
Abstract
Background/aims: We characterised the relationships between monitoring frequency, ranibizumab injection need and vision in patients receiving as-needed (pro re nata; PRN) ranibizumab for macular oedema due to branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) or central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) in this post-hoc analysis of SHORE and HORIZON.
Methods: Patients aged 18 years and older with macular oedema due to BRVO/CRVO were included in this analysis. Injection frequency and best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were evaluated by PRN injection frequency in the PRN dosing phase (months (M) 7-15) of SHORE and through 12 months of HORIZON. Prespecified PRN re-treatment criteria for each trial were based on protocol-prespecified BCVA and optical coherence tomography outcomes.
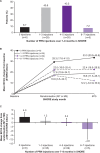
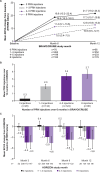
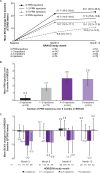
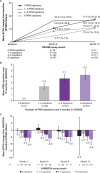
Results: After the initial 7 monthly ranibizumab injections, patients in SHORE gained a mean of 18.3 letters from baseline. Patients randomised to PRN, on average, maintained these gains. However, some patients experienced additional mean gains, whereas others suffered losses (range 4.0 (95% CI 0.7 to 7.3) to -4.6 (95% CI -11.8 to 2.6) letters in patients who received 0 and 6-7 PRN injections, respectively). In BRAVO and CRUISE (lead-in trials), patients experienced mean gains from baseline to M6 (monthly dosing) of 19.3 and 15.0 letters, respectively, with gains maintained with PRN from M6 to M12. However, mean BCVA changes from baseline to M12 varied in HORIZON (range -0.4 (95% CI -2.5 to 1.6) to -3.6 (95% CI -6.2 to -1.0) letters in patients who received zero and six injections, respectively, during the preceding PRN phase of BRAVO and CRUISE).
Conclusion: The BRVO/CRVO population is heterogenous with a varied response to ranibizumab treatment.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Clinical Trial; Macula; Retina; Treatment Medical.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RBB is a consultant for Rezolute, Ribomic, Unity Bio and Visgenx; receives financial support from Genentech, Inc. and NGM Bio; and holds a patent or personal financial interest in Oculinea. PAC is an advisory board member for Aerpio, Allegro, Applied Genetic Technologies Corporation, Exonate, Merck and Roche/Genentech, Inc.; co-founder of Graybug Vision; consultant for AsclepiX, Bausch + Lomb, CureVac, Graybug Vision, Novartis, Perfuse Therapeutics and Wave Life Sciences; and investigator for Aerpio, Oxford Biomedica, Regeneron, Regenxbio, Roche/Genentech, Inc. and Sanofi Genzyme. SB, CQ-R and ZH are employees of Genentech, Inc. ML indicates no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lucentis [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, Inc, 2018.
-
- Eylea [package insert]. Tarrytown, NY: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc, 2021.
-
- Lucentis [summary of product characteristics]. Dublin, Ireland: Novartis Europharm Limited, 2022.
-
- Eylea [summary of product characteristics]. Leverkusen, Germany: Bayer AG, 2022.
