The crystal structure of SUN1-KASH6 reveals an asymmetric LINC complex architecture compatible with nuclear membrane insertion
- PMID: 38291267
- PMCID: PMC10827754
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-05794-6
The crystal structure of SUN1-KASH6 reveals an asymmetric LINC complex architecture compatible with nuclear membrane insertion
Abstract
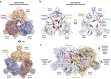
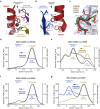
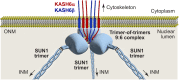
The LINC complex transmits cytoskeletal forces into the nucleus to control the structure and movement of nuclear contents. It is formed of nuclear SUN and cytoplasmic KASH proteins, which interact within the nuclear lumen, immediately below the outer nuclear membrane. However, the symmetrical location of KASH molecules within SUN-KASH complexes in previous crystal structures has been difficult to reconcile with the steric requirements for insertion of their immediately upstream transmembrane helices into the outer nuclear membrane. Here, we report the crystal structure of the SUN-KASH complex between SUN1 and JAW1/LRMP (KASH6) in an asymmetric 9:6 configuration. This intertwined assembly involves two distinct KASH conformations such that all six KASH molecules emerge on the same molecular surface. Hence, they are ideally positioned for insertion of upstream sequences into the outer nuclear membrane. Thus, we report a SUN-KASH complex architecture that appears to be directly compatible with its biological role.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Conserved SUN-KASH Interfaces Mediate LINC Complex-Dependent Nuclear Movement and Positioning.Curr Biol. 2018 Oct 8;28(19):3086-3097.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 30245107 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular mechanism for LINC complex branching by structurally diverse SUN-KASH 6:6 assemblies.Elife. 2021 Jan 4;10:e60175. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60175. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33393904 Free PMC article.
-
Connecting the nucleus to the cytoskeleton by SUN-KASH bridges across the nuclear envelope.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;25(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23149102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A synthetic biology platform for the reconstitution and mechanistic dissection of LINC complex assembly.J Cell Sci. 2018 Oct 31;132(4):jcs219451. doi: 10.1242/jcs.219451. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30262467
-
Interactions between nuclei and the cytoskeleton are mediated by SUN-KASH nuclear-envelope bridges.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:421-44. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100109-104037. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20507227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging mechanomedicines informed by mechanotransduction along the integrin-cytoskeleton-nucleus axis.APL Bioeng. 2025 Jun 10;9(2):021503. doi: 10.1063/5.0255473. eCollection 2025 Jun. APL Bioeng. 2025. PMID: 40502441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Life outside the LINC complex - Do SUN proteins have LINC-independent functions?Bioessays. 2024 Aug;46(8):e2400034. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400034. Epub 2024 May 27. Bioessays. 2024. PMID: 38798157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Structure, Size Regulation, and Role in Cell Migration.Cells. 2024 Dec 23;13(24):2130. doi: 10.3390/cells13242130. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39768219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

