When sequential use of mepolizumab and dupilumab in a severe atopic eosinophilic asthmatic questions the role of eosinophils in mediating the clinical expression of the disease: a case report
- PMID: 38291489
- PMCID: PMC10829233
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-023-04255-8
When sequential use of mepolizumab and dupilumab in a severe atopic eosinophilic asthmatic questions the role of eosinophils in mediating the clinical expression of the disease: a case report
Abstract
Background: The advent of biologics has resulted in major progress in the treatment of severe T2 high asthmatics. There are currently several classes of biologics approved for severe asthma including anti-immunoglobulin E, anti-interleukin-5/interleukin 5R, anti-interleukin 4/interleukin 13R, and anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
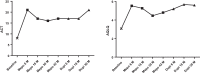
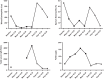
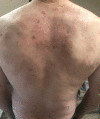
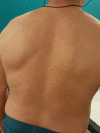
Case presentations: Here we report the case of a 55-year-old Caucasian man with severe eosinophilic atopic asthma, who sequentially benefited from a treatment with mepolizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 monoclonal antibody, followed by treatment with dupilumab, an anti-interleukin-4/interleukin-13R antibody, the switch being justified by a flare-up of dermatitis while on mepolizumab. Overall, the patient has been followed for 72 months, including 42 months on mepolizumab and 30 months on dupilumab. Close monitoring of exacerbations, asthma control, lung function, asthma quality of life, and biomarkers shows that both biologics reduced asthma exacerbation and provided an improvement in asthma control and quality of life, with the patient achieving remission after 30 months on dupilumab. However, the effects of the two biologics on the biomarkers were very different, with mepolizumab controlling eosinophilic inflammation and dupilumab reducing serum immunoglobulin E and fractional exhaled nitric oxide levels.
Conclusion: The originality of this case resides in the description of clinical status and biomarker evolution after a sequential use of mepolizumab and dupilumab in a severe atopic eosinophilic asthmatic. It shows that mepolizumab reduces exacerbation and improves asthma control by curbing eosinophilic inflammation whereas dupilumab provides asthma remission without controlling airway eosinophilic inflammation.
Keywords: Asthma; Dupilumab; Eosinophils; FeNO; IgE; Mepolizumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R. Louis reports grants and personal fees from GSK, AZ, Chiesi, and Novartis and personal fees from Sanofi outside the submitted work. F. Schleich reports grants and personal fees for national board participation and presentations from GSK and AstraZeneca and personal fees for board participation and lectures from Chiesi outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Agache I, Beltran J, Akdis C, Akdis M, Canelo-Aybar C, WalterCanonica G, Casale T, Chivato T, Corren J, Del Giacco S, Eiwegger T, Firinu D, Gern JE, Hamelmann E, Hanania N, Mäkelä M, Hernandez-Martin I, Nair P, O’Mahony L, Papadopoulos NG, Papi A, Park H-S, Perez de Liano L, Posso M, Rocha C, Quirce S, Sastre J, Shamji M, Song Y, Steiner C, Schwarze J, Alonso-Coello P, Palomares O, Jutel M. Efficacy and safety of treatment with biologicals (benralizumab, dupilumab and omalizumab) for severe allergic asthma: a systematic review for the EAACI Guidelines—recommendations on the use of biologicals in severe asthma. Allergy. 2020;75(5):1043–1057. doi: 10.1111/all.14235. - DOI - PubMed

