Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Protein 2 Inhibitors: Novel Application for the Treatment of Obesity-Associated Hypertension
- PMID: 38292009
- PMCID: PMC10826576
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S446904
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Protein 2 Inhibitors: Novel Application for the Treatment of Obesity-Associated Hypertension
Abstract
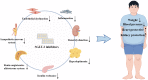
Obesity is becoming increasingly prevalent in China and worldwide and is closely related to the development of hypertension. The pathophysiology of obesity-associated hypertension is complex, including an overactive sympathetic nervous system (SNS), activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), insulin resistance, hyperleptinemia, renal dysfunction, inflammatory responses, and endothelial function, which complicates treatment. Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, novel hypoglycemic agents, have been shown to reduce body weight and blood pressure and may serve as potential novel agents for the treatment of obesity-associated hypertension. This review discusses the beneficial mechanisms of SGLT-2 inhibitors for the treatment of obesity-associated hypertension. SGLT-2 inhibitors can inhibit SNS activity, reduce RAAS activation, ameliorate insulin resistance, reduce leptin secretion, improve renal function, and inhibit inflammatory responses. SGLT-2 inhibitors can, therefore, simultaneously target multiple mechanisms of obesity-associated hypertension and may serve as an effective treatment for obesity-associated hypertension.
Keywords: inflammation; metabolism; neuro-humoral regulation; obesity-associated hypertension; sodium-glucose cotransporter protein 2 inhibitors.
© 2024 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypertension as a Metabolic Disorder and the Novel Role of the Gut.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019 Jun 24;21(8):63. doi: 10.1007/s11906-019-0964-5. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019. PMID: 31236708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship Between the Blood-Brain-Barrier and the Central Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Aug 22;15:2583-2597. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S375559. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 36035518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity-associated cardiometabolic complications in polycystic ovary syndrome: The potential role of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 15;14:951099. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.951099. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36875461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity-induced hypertension: interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms.Circ Res. 2015 Mar 13;116(6):991-1006. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305697. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 25767285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The mechanisms and clinical potential: sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors treating diabetic kidney disease].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2018 Dec 25;70(6):663-669. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 30560277 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Blood pressure reduction with empagliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases: a post-hoc sub-analysis of the placebo-controlled randomized EMBLEM trial.Hypertens Res. 2024 Sep;47(9):2295-2302. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01725-4. Epub 2024 May 24. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38789538 Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors: Focus on Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 15;26(4):1670. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041670. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang Y, Zhao L, Gao L, Pan A, Xue H. Health policy and public health implications of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(7):446–461. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

