Case report: Significance of the large rhomboid lip in microvascular decompression: insights from two clinical cases
- PMID: 38292034
- PMCID: PMC10825857
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1336273
Case report: Significance of the large rhomboid lip in microvascular decompression: insights from two clinical cases
Abstract
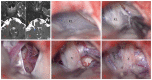
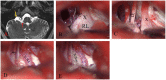
The rhomboid lip (RL) is a layer of neural tissue that extends outside the fourth ventricle and is connected to the lateral recess of the fourth ventricle. Although this anatomical structure has been rigorously studied, it is often overlooked in microvascular decompression (MVD) surgery. In this report, we present two cases, one of hemifacial spasm (HFS) and one of glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GPN), in which a large RL was observed during surgery. We found that a large RL is easily confused with arachnoid cysts, and accurate identification and dissection are important to protect the lower cranial nerves.
Keywords: flocculus; glossopharyngeal neuralgia; hemifacial spasm; microvascular decompression; rhomboid lip.
Copyright © 2024 Ding, Li, Zuo, Song, Xiao, Wang, Geng, Hu, Yang, Liu and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Importance of awareness of the rhomboid lip in microvascular decompression surgery for hemifacial spasm.J Neurosurg. 2013 Oct;119(4):1038-42. doi: 10.3171/2013.4.JNS121546. Epub 2013 May 24. J Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 23706056
-
Fully endoscopic microvascular decompression for the treatment of hemifacial spasm, trigeminal neuralgia, and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a retrospective study.BMC Surg. 2023 Oct 27;23(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02214-0. BMC Surg. 2023. PMID: 37891595 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion of rhomboid lip to lower cranial nerves as special consideration in microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm: Report of two cases.Surg Neurol Int. 2010 Nov 18;1:71. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.72581. Surg Neurol Int. 2010. PMID: 21170363 Free PMC article.
-
A Unique Case of Microvascular Triple Decompression for Combined Simultaneous Trigeminal Neuralgia, Hemifacial Spasm, and Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia Because of the Dolichoectatic Vertebrobasilar System.Oper Neurosurg. 2020 Jun 1;18(6):692-697. doi: 10.1093/ons/opz205. Oper Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31334555 Review.
-
A Meta-Analysis of Endoscopic Microvascular Decompression versus Microscopic Microvascular Decompression for the Treatment for Cranial Nerve Syndrome Caused by Vascular Compression.World Neurosurg. 2019 Jun;126:647-655.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.220. Epub 2019 Feb 15. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30776512
Cited by
-
Myasthenia gravis in 2025: five new things and four hopes for the future.J Neurol. 2025 Feb 22;272(3):226. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-12922-7. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39987373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anatomical considerations and surgical manipulation of the rhomboid lip in microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024 Jun 8;166(1):255. doi: 10.1007/s00701-024-06155-2. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024. PMID: 38850321
-
Impact of offending vessel location on lateral spread response variations in hemifacial spasm patients.Front Neurol. 2025 Mar 25;16:1561134. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1561134. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40201021 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes following posterior fossa decompression in pediatric patients with Chiari malformation type 1, a population-based cohort study.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024 Nov 18;166(1):460. doi: 10.1007/s00701-024-06332-3. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024. PMID: 39551853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hitotsumatsu T, Matsushima T, Inoue T. Microvascular decompression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm, and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: three surgical approach variations: technical note. Neurosurgery. (2003) 53:1436–41; discussion: 42–3. 10.1227/01.neu.0000093431.43456.3b - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

