Machine Learning Bolsters Evidence That D1, Nef, and Tat Influence HIV Reservoir Dynamics
- PMID: 38292079
- PMCID: PMC10827039
- DOI: 10.20411/pai.v8i2.621
Machine Learning Bolsters Evidence That D1, Nef, and Tat Influence HIV Reservoir Dynamics
Abstract
Background: The primary hurdle to curing HIV is due to the establishment of a reservoir early in infection. In an effort to find new treatment strategies, we and others have focused on understanding the selection pressures exerted on the reservoir by studying how proviral sequences change over time.
Methods: To gain insights into the dynamics of the HIV reservoir we analyzed longitudinal near full-length sequences from 7 people living with HIV between 1 and 20 years following the initiation of antiretroviral treatment. We used this data to employ Bayesian mixed effects models to characterize the decay of the reservoir using single-phase and multiphasic decay models based on near full-length sequencing. In addition, we developed a machine-learning approach utilizing logistic regression to identify elements within the HIV genome most associated with proviral decay and persistence. By systematically analyzing proviruses that are deleted for a specific element, we gain insights into their role in reservoir contraction and expansion.
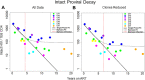
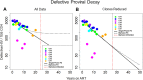
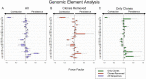
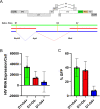
Results: Our analyses indicate that biphasic decay models of intact reservoir dynamics were better than single-phase models with a stronger statistical fit. Based on the biphasic decay pattern of the intact reservoir, we estimated the half-lives of the first and second phases of decay to be 18.2 (17.3 to 19.2, 95%CI) and 433 (227 to 6400, 95%CI) months, respectively.In contrast, the dynamics of defective proviruses differed favoring neither model definitively, with an estimated half-life of 87.3 (78.1 to 98.8, 95% CI) months during the first phase of the biphasic model. Machine-learning analysis of HIV genomes at the nucleotide level revealed that the presence of the splice donor site D1 was the principal genomic element associated with contraction. This role of D1 was then validated in an in vitro system. Using the same approach, we additionally found supporting evidence that HIV nef may confer a protective advantage for latently infected T cells while tat was associated with clonal expansion.
Conclusions: The nature of intact reservoir decay suggests that the long-lived HIV reservoir contains at least 2 distinct compartments. The first compartment decays faster than the second compartment. Our machine-learning analysis of HIV proviral sequences reveals specific genomic elements are associated with contraction while others are associated with persistence and expansion. Together, these opposing forces shape the reservoir over time.
Keywords: HIV Reservoir; Machine Learning; NFL Sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 Pathogens and Immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Trickey A, Sabin CA, Burkholder G, Crane H, d'Arminio Monforte A, Egger M, Gill MJ, Grabar S, Guest JL, Jarrin I, Lampe FC, Obel N, Reyes JM, Stephan C, Sterling TR, Teira R, Touloumi G, Wasmuth JC, Wit F, Wittkop L, Zangerle R, Silverberg MJ, Justice A, Sterne JAC.. Life expectancy after 2015 of adults with HIV on long-term antiretroviral therapy in Europe and North America: a collaborative analysis of cohort studies. The Lancet HIV. 2023;10(5): e295-e307. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(23)00028-0. Epub 2023 Mar 20. PMID: 36958365; PMCID: PMC10288029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Finzi D, Hermankova M, Pierson T, Carruth LM, Buck C, Chaisson RE, Quinn TC, Chadwick K, Margolick J, Brookmeyer R, Gallant J, Markowitz M, Ho DD, Rich-man DD, Siliciano RF.. Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science. 1997;278(5341):1295-1300. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1295. PMID: 9360927. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chun TW, Carruth L, Finzi D, Shen X, DiGiuseppe JA, Taylor H, Hermankova M, Chadwick K, Margolick J, Quinn TC, Kuo YH, Brookmeyer R, Zeiger MA, Bar-ditch-Crovo P, Siliciano RF.. Quantification of latent tissue reservoirs and total body viral load in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1997;387(6629):183-188. doi: 10.1038/387183a0. PMID: 9144289. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Laskey SB, Pohlmeyer CW, Bruner KM, Siliciano RF.. Evaluating Clonal Expansion of HIV-Infected Cells: Optimization of PCR Strategies to Predict Clonality. PLoS Pathogens. 2016;12(8):1-17. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005689. PMID: 27494508; PMCID: PMC4975415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
