Comparative assessment of regulated methods and PCR in the diagnosis of trichophytosis in veterinary mycology
- PMID: 38292703
- PMCID: PMC10824085
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i12.11
Comparative assessment of regulated methods and PCR in the diagnosis of trichophytosis in veterinary mycology
Abstract
Background: There is an increase in the incidence of human and animal infectious skin diseases of fungal etiology in the world. The main source of infecting the population has become agricultural and stray animals.
Aim: The objective of this study was to examine the morphophysiological and microbiological characteristics of pathogenic fungi belonging to the species Trichophyton verrucosum. This species is known to cause diseases in both humans and livestock in Kazakhstan. In addition, the study aimed to assess the feasibility of using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for detecting T. verrucosum. This assessment was conducted in comparison to the outcomes of conventional laboratory diagnostic tests commonly employed for trichophytosis.
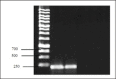
Methods: The research focused on analyzing 141 samples of pathological material obtained from calves in Almaty, Turkestan, and Kyzylorda regions. These calves exhibited clinical symptoms of skin disease. The study aimed to identify the causative agent using various techniques, including microscopic examination, microbiological methods involving the isolation of pure cultures, and PCR.
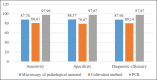
Results: The detection of the causative agent of dermatophytosis using conventional methods was relatively low, 86% for the microscopic method, and 79% for the microbiological method with the isolation of the culture of the pathogen. Extraction and detection of the genetic material of the causative agent of the disease for PCR was carried out according to the method developed by the authors. The effectiveness of the PCR method was 97.9%, which is significantly higher (p < 0.05) compared with the diagnostic effectiveness of conventional methods. The PCR method using specific primers identified the causative agent in 98% of cases, which significantly (p < 0.05) exceeded the results obtained using conventional diagnostic methods. Accordingly, the PCR method had better sensitivity and specificity indicators.
Conclusion: The conducted study recommends the method of PCR diagnosis of dermatophytosis for fast and reliable confirmation of the diagnosis of dermatophytosis in humans and animals in Kazakhstan.
Keywords: Dermatophytosis; Fungal cultivation; Microscopy; Molecular detection; Prognostic predictive value.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PCR-terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism for direct detection and identification of dermatophytes in veterinary mycology.Med Mycol. 2019 Jun 1;57(4):447-456. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myy058. Med Mycol. 2019. PMID: 30085212
-
Ringworm in calves: risk factors, improved molecular diagnosis, and therapeutic efficacy of an Aloe vera gel extract.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Nov 4;16(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02616-9. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 33148275 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of strains of the Trichophyton verrucosum complex from Tunisia.Med Mycol. 2016 Nov 1;54(8):787-93. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myw036. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Med Mycol. 2016. PMID: 27364650
-
Deep facial mycosis due to Trichophyton verrucosum-molecular genetic identification of the dermatophyte in paraffin-embedded tissue-case report and review of the literature.Mycoses. 2018 Mar;61(3):152-158. doi: 10.1111/myc.12719. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Mycoses. 2018. PMID: 29082569 Review.
-
Multiplex RT-PCR provides improved diagnosis of skin and nail dermatophyte infections compared to microscopy and culture: a laboratory study and review of the literature.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Nov;101(3):115413. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115413. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34256251 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics of Chrysosporium spp. Pathogens Causing Skin Mycoses in Horses.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Apr 9;11(4):297. doi: 10.3390/jof11040297. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278119 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and application of multiplex PCR method for detection of Trichophyton verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Trichophyton mentagrophytes from cattle.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 24;12:1546586. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1546586. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40196810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 24.kz. The number of cases of dermatophytosis is growing in Kyzylorda. 2022 Available via https://24.kz/ru/news/social/item/549044-kolichestvo-sluchaev-dermatomik... .
-
- Akhmetov K.K, Chidunchi I.Y. Structural organization of muscular elements of a skin-muscular sac of trematodes: literature survey. Int. J. Zool. Res. 2015;11(1):1–8.
-
- Álvarez-Mosquera I, Hernáez S, Sánchez J, Suárez M.D, Cisterna R. Diagnosis of superficial mycoses by a rapid and effective PCR method from samples of scales, nails and hair. Mycopathologia. 2018;183(5):777–783. - PubMed
-
- Aruna G.L, Ramalingappa B. Development of indirect ELISA and its evaluation in comparison with KOH hydrolysis and fungal culture for the immuno diagnosis of Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes infection in humans. Acta Trop. 2022;235:106590. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical