This is a preprint.
A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types
- PMID: 38293118
- PMCID: PMC10827189
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.15.575757
A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types
Update in
-
A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types.Genome Res. 2024 Sep 20;34(8):1235-1252. doi: 10.1101/gr.278980.124. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39142810 Free PMC article.
Abstract
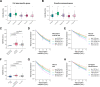
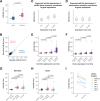
During embryonic development, cells undergo dynamic changes in gene expression that are required for appropriate cell fate specification. Although both transcription and mRNA degradation contribute to gene expression dynamics, patterns of mRNA decay are less well-understood. Here we directly measured spatiotemporally resolved mRNA decay rates transcriptome-wide throughout C. elegans embryogenesis by transcription inhibition followed by bulk and single-cell RNA-sequencing. This allowed us to calculate mRNA half-lives within specific cell types and developmental stages and identify differentially regulated mRNA decay throughout embryonic development. We identified transcript features that are correlated with mRNA stability and found that mRNA decay rates are associated with distinct peaks in gene expression over time. Moreover, we provide evidence that, on average, mRNA is more stable in the germline compared to in the soma and in later embryonic stages compared to in earlier stages. This work suggests that differential mRNA decay across cell states and time helps to shape developmental gene expression, and it provides a valuable resource for studies of mRNA turnover regulatory mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types.Genome Res. 2024 Sep 20;34(8):1235-1252. doi: 10.1101/gr.278980.124. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39142810 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation of mRNA decay during neural development.Neural Dev. 2015 Apr 21;10:11. doi: 10.1186/s13064-015-0038-6. Neural Dev. 2015. PMID: 25896902 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of mRNA decay patterns during early Drosophila development.Genome Biol. 2010;11(9):R93. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-9-r93. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20858238 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic mRNA decay: methodologies, pathways, and links to other stages of gene expression.J Mol Biol. 2013 Oct 23;425(20):3750-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.02.029. Epub 2013 Mar 4. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23467123 Review.
-
Messenger RNA decay during aging and development.Ageing Res Rev. 2002 Sep;1(4):607-25. doi: 10.1016/s1568-1637(02)00023-5. Ageing Res Rev. 2002. PMID: 12208236 Review.
References
-
- Angeles-Albores D, Lee RYN, Chan J, Sternberg PW. 2018. Mar 2. Two new functions in the WormBase Enrichment Suite. MicroPublication Biol. doi:10.17912/W25Q2N. [accessed 2023 Apr 13]. https://www.micropublication.org/journals/biology/w25q2n. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
