This is a preprint.
An unconventional regulatory circuitry involving Aurora B controls anaphase onset and error-free chromosome segregation in trypanosomes
- PMID: 38293145
- PMCID: PMC10827227
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.20.576407
An unconventional regulatory circuitry involving Aurora B controls anaphase onset and error-free chromosome segregation in trypanosomes
Update in
-
Aurora B controls anaphase onset and error-free chromosome segregation in trypanosomes.J Cell Biol. 2024 Nov 4;223(11):e202401169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202401169. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39196069 Free PMC article.
Abstract
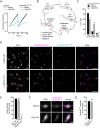
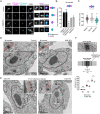
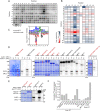
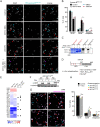
Accurate chromosome segregation during mitosis requires that all chromosomes establish stable bi-oriented attachments with the spindle apparatus. Kinetochores form the interface between chromosomes and spindle microtubules and as such are under tight control by complex regulatory circuitry. As part of the chromosomal passenger complex (CPC), the Aurora B kinase plays a central role within this circuitry by destabilizing improper kinetochore-microtubule attachments and relaying the attachment status to the spindle assembly checkpoint, a feedback control system that delays the onset of anaphase by inhibiting the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. Intriguingly, Aurora B is conserved even in kinetoplastids, an evolutionarily divergent group of eukaryotes, whose kinetochores are composed of a unique set of structural and regulatory proteins. Kinetoplastids do not have a canonical spindle checkpoint and it remains unclear how their kinetochores are regulated to ensure the fidelity and timing of chromosome segregation. Here, we show in Trypanosoma brucei, the kinetoplastid parasite that causes African sleeping sickness, that inhibition of Aurora B using an analogue-sensitive approach arrests cells in metaphase, with a reduction in properly bi-oriented kinetochores. Aurora B phosphorylates several kinetochore proteins in vitro, including the N-terminal region of the divergent Bub1-like protein KKT14. Depletion of KKT14 partially overrides the cell cycle arrest caused by Aurora B inhibition, while overexpression of a non-phosphorylatable KKT14 protein results in a prominent delay in the metaphase-to-anaphase transition. Finally, we demonstrate using a nanobody-based system that re-targeting the catalytic module of the CPC to the outer kinetochore is sufficient to promote mitotic exit but causes massive chromosome mis-segregation in anaphase. Our results indicate that the CPC and KKT14 are involved in an unconventional pathway controlling mitotic exit and error-free chromosome segregation in trypanosomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aurora B controls anaphase onset and error-free chromosome segregation in trypanosomes.J Cell Biol. 2024 Nov 4;223(11):e202401169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202401169. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39196069 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetoplastid kinetochore proteins KKT14-KKT15 are divergent Bub1/BubR1-Bub3 proteins.Open Biol. 2024 Jun;14(6):240025. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240025. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 38862021 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic localization of the chromosomal passenger complex in trypanosomes is controlled by the orphan kinesins KIN-A and KIN-B.Elife. 2024 Apr 2;13:RP93522. doi: 10.7554/eLife.93522. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38564240 Free PMC article.
-
Killing two birds with one stone: how budding yeast Mps1 controls chromosome segregation and spindle assembly checkpoint through phosphorylation of a single kinetochore protein.Curr Genet. 2020 Dec;66(6):1037-1044. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01091-x. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32632756 Review.
-
Detection and correction of merotelic kinetochore orientation by Aurora B and its partners.Cell Cycle. 2007 Jul 1;6(13):1558-64. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.13.4452. Epub 2007 May 18. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17603301 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
