This is a preprint.
Cbfβ regulates Wnt/β-catenin, Hippo/Yap, and TGFβ signaling pathways in articular cartilage homeostasis and protects from ACLT surgery-induced osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38293189
- PMCID: PMC10827176
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.15.575763
Cbfβ regulates Wnt/β-catenin, Hippo/Yap, and TGFβ signaling pathways in articular cartilage homeostasis and protects from ACLT surgery-induced osteoarthritis
Update in
-
Cbfβ regulates Wnt/β-catenin, Hippo/Yap, and Tgfβ signaling pathways in articular cartilage homeostasis and protects from ACLT surgery-induced osteoarthritis.Elife. 2024 May 28;13:e95640. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95640. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38805545 Free PMC article.
Abstract
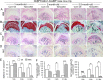
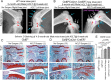
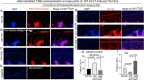
As the most common degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) contributes significantly to pain and disability during aging. Several genes of interest involved in articular cartilage damage in OA have been identified. However, the direct causes of OA are poorly understood. Evaluating the public human RNA-seq dataset showed that Cbfβ, (subunit of a heterodimeric Cbfβ/Runx1,Runx2, or Runx3 complex) expression is decreased in the cartilage of patients with OA. Here, we found that the chondrocyte-specific deletion of Cbfβ in tamoxifen-induced Cbfβf/fCol2α1-CreERT mice caused a spontaneous OA phenotype, worn articular cartilage, increased inflammation, and osteophytes. RNA-sequencing analysis showed that Cbfβ deficiency in articular cartilage resulted in reduced cartilage regeneration, increased canonical Wnt signaling and inflammatory response, and decreased Hippo/YAP signaling and TGF-β signaling. Immunostaining and western blot validated these RNA-seq analysis results. ACLT surgery-induced OA decreased Cbfβ and Yap expression and increased active β-catenin expression in articular cartilage, while local AAV-mediated Cbfβ overexpression promoted Yap expression and diminished active β-catenin expression in OA lesions. Remarkably, AAV-mediated Cbfβ overexpression in knee joints of mice with OA showed the significant protective effect of Cbfβ on articular cartilage in the ACLT OA mouse model. Overall, this study, using loss-of-function and gain-of-function approaches, uncovered that low expression of Cbfβ may be the cause of OA. Moreover, Local admission of Cbfβ may rescue and protect OA through decreasing Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and increasing Hippo/Yap signaling and TGFβ/Smad2/3 signaling in OA articular cartilage, indicating that local Cbfβ overexpression could be an effective strategy for treatment of OA.
Keywords: AAV mediated treatment of osteoarthritis; Cbfβ; Osteoarthritis; TGF-β signaling; Wnt signaling; YAP signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Cbfβ regulates Wnt/β-catenin, Hippo/Yap, and Tgfβ signaling pathways in articular cartilage homeostasis and protects from ACLT surgery-induced osteoarthritis.Elife. 2024 May 28;13:e95640. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95640. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38805545 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Cbfβ in articular cartilage leads to osteoarthritis-like phenotype through Hippo/Yap, TGFβ, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Mar 11;20(6):1965-1977. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.90250. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38617544 Free PMC article.
-
Runx1 is a key regulator of articular cartilage homeostasis by orchestrating YAP, TGFβ, and Wnt signaling in articular cartilage formation and osteoarthritis.Bone Res. 2022 Oct 28;10(1):63. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00231-y. Bone Res. 2022. PMID: 36307389 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of the Hippo-YAP signalling pathway in Cartilage and Osteoarthritis.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Sep;90:102015. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102015. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 37454824 Review.
-
Cbfβ: A key regulator in skeletal stem cell differentiation, bone development, and disease.FASEB J. 2025 Feb 28;39(4):e70399. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500030R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 39996474 Review.
References
-
- Aini H, Itaka K, Fujisawa A, Uchida H, Uchida S, Fukushima S, Kataoka K, Saito T, Chung UI, Ohba S. Messenger RNA delivery of a cartilage-anabolic transcription factor as a disease-modifying strategy for osteoarthritis treatment. Scientific reports. 2016;6:18743. Epub 2016/01/06. doi: 10.1038/srep18743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
