Critical importance of patient-reported outcomes for a comprehensive assessment of psoriatic arthritis patients
- PMID: 38293304
- PMCID: PMC10826607
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1332432
Critical importance of patient-reported outcomes for a comprehensive assessment of psoriatic arthritis patients
Abstract
Introduction: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a heterogeneous, chronic inflammatory disease that negatively impacts patients' quality of life. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) are used to capture patient perspectives in disease assessment, and physicians use the Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA) to evaluate disease activity in PsA. The study aimed to assess the relationship between PROMs and the DAPSA score in consecutive outpatients affected by PsA.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted from March 2018 to October 2020 at the PsA clinic of the ARNAS Civico in Palermo (Italy), enrolling outpatients with PsA. Patients were assessed for their disease activity according to the DAPSA score, and PROMs, such as PHQ-9, HAQ, FACIT-F, and PsAID, were evaluated. Linear regression analysis evaluated the relationship between the DAPSA Score and the included PROMs.
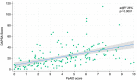
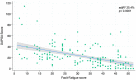
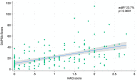
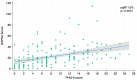
Results: 158 PsA consecutive peripheral subset psoriatic arthritis outpatients were recruited. The median years of illness was 10.6 (9.3-11.9), and the median DAPSA score was 19.02 (9-33.1). The regression analysis highlighted a strong relationship between the DAPSA score and the PsAID (adjR2 26%, p < 0.0001), the FACIT-F (adjR2 25.4%, p < 0.0001), the HAQ (adjR2 23.7%, p < 0.0001), and PHQ-9 (adjR2 15%, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: PROMs are strongly associated with the DAPSA score, but it allows in-depth evaluation of the impact of the disease on different domains of PsA patients' life.
Keywords: disease activity; multidimensional assessment; nurse assessment; nursing; patient reported outcomes; psoriatic disease; quality of life; rheumatology.
Copyright © 2024 Lo Monaco, Mallaci Bocchio, Natoli, Giardina, Cangemi, Scibetta, Argano and Corrao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous