Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate regulates anti-tumor immunity
- PMID: 38293535
- PMCID: PMC10826830
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24454
Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate regulates anti-tumor immunity
Abstract
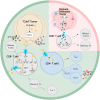
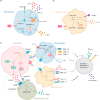
"Oncometabolite" 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) is an aberrant metabolite found in tumor cells, exerting a pivotal influence on tumor progression. Recent studies have unveiled its impact on the proliferation, activation, and differentiation of anti-tumor T cells. Moreover, 2-HG regulates the function of innate immune components, including macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and the complement system. Elevated levels of 2-HG hinder α-KG-dependent dioxygenases (α-KGDDs), contributing to tumorigenesis by disrupting epigenetic regulation, genome integrity, hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) signaling, and cellular metabolism. The chiral molecular structure of 2-HG produces two enantiomers: D-2-HG and L-2-HG, each with distinct origins and biological functions. Efforts to inhibit D-2-HG and leverage the potential of L-2-HG have demonstrated efficacy in cancer immunotherapy. This review delves into the metabolism, biological functions, and impacts on the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) of 2-HG, providing a comprehensive exploration of the intricate relationship between 2-HG and antitumor immunity. Additionally, we examine the potential clinical applications of targeted therapy for 2-HG, highlighting recent breakthroughs as well as the existing challenges.
Keywords: 2-Hydroxyglutarate; Isocitrate dehydrogenase; Oncometabolite; Therapeutic target; Tumor immune microenvironment.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures