Decoding the regulatory landscape of lncRNAs as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric and colorectal cancers
- PMID: 38294554
- PMCID: PMC10830721
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-023-01260-5
Decoding the regulatory landscape of lncRNAs as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric and colorectal cancers
Abstract
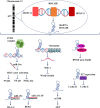
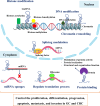
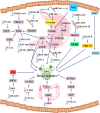
Colorectal cancer (CRC) and gastric cancer (GC) are major contributors to cancer-related mortality worldwide. Despite advancements in understanding molecular mechanisms and improved drug treatments, the overall survival rate for patients remains unsatisfactory. Metastasis and drug resistance are major challenges contributing to the high mortality rate in both CRC and GC. Recent research has shed light on the role of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the development and progression of these cancers. LncRNAs regulate gene expression through various mechanisms, including epigenetic modifications and interactions with microRNAs (miRNAs) and proteins. They can serve as miRNA precursors or pseudogenes, modulating gene expression at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Additionally, circulating lncRNAs have emerged as non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction of drug therapy response in CRC and GC. This review explores the intricate relationship between lncRNAs and CRC/GC, encompassing their roles in cancer development, progression, and chemoresistance. Furthermore, it discusses the potential of lncRNAs as therapeutic targets in these malignancies. The interplay between lncRNAs, miRNAs, and tumor microenvironment is also highlighted, emphasizing their impact on the complexity of cancer biology. Understanding the regulatory landscape and molecular mechanisms governed by lncRNAs in CRC and GC is crucial for the development of effective diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, as well as novel therapeutic strategies. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge and paves the way for further exploration of lncRNAs as key players in the management of CRC and GC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Drug resistance; Gastric cancer; Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA); Therapeutic targets.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deciphering the functional landscape and therapeutic implications of noncoding RNAs in the TGF-β signaling pathway in colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Mar;255:155158. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155158. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38320438 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5226-39. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6446. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26637808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs and lncRNAs serve as biomarkers for early colorectal cancer diagnosis.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Mar;255:155187. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155187. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38377721
-
Unraveling the influence of LncRNA in gastric cancer pathogenesis: a comprehensive review focus on signaling pathways interplay.Med Oncol. 2024 Aug 5;41(9):218. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02455-w. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39103705 Review.
-
The emerging role of noncoding RNAs in colorectal cancer chemoresistance.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019 Dec;42(6):757-768. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00466-8. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019. PMID: 31359293 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic combinations of exosomes alongside cancer stem cells (CSCs) and of CSC-derived exosomes (CSCEXs) in cancer therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 5;24(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03514-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39369258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of DNA Methylation and RNA Interference in Gastric Cancer: A 2024 Update.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 3;12(9):2001. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092001. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the development and progression of long non-coding RNA in upper gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 1;16(1):980. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02800-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40450604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in Stomach Cancer Burden in China: A Joinpoint and APC Analysis Based on GBD 2021.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun;40(6):1500-1514. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16956. Epub 2025 Apr 1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40166947 Free PMC article.
-
ncRNAs as Key Regulators in Gastric Cancer: From Molecular Subtyping to Therapeutic Targets.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Aug;32(8):6080-6097. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-17368-9. Epub 2025 May 13. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40358781 Review.
References
-
- Esmaeili M, Keshani M, Vakilian M, Esmaeili M, Peymani M, Seyed Forootan F, et al. Role of non-coding RNAs as novel biomarkers for detection of colorectal cancer progression through interaction with the cell signaling pathways. Gene. 2020;753: 144796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

