Time-resolved chemical monitoring of whole plant roots with printed electrochemical sensors and machine learning
- PMID: 38295162
- PMCID: PMC10830104
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adj6315
Time-resolved chemical monitoring of whole plant roots with printed electrochemical sensors and machine learning
Abstract
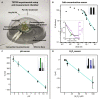
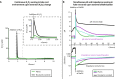
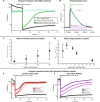
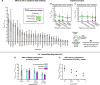
Traditional single-point measurements fail to capture dynamic chemical responses of plants, which are complex, nonequilibrium biological systems. We report TETRIS (
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plant-on-a-chip: continuous, soilless electrochemical monitoring of salt uptake and tolerance among different genotypes of tomato.Sens Diagn. 2024 Apr 11;3(5):799-808. doi: 10.1039/d4sd00065j. eCollection 2024 May 16. Sens Diagn. 2024. PMID: 38766392 Free PMC article.
-
Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization.J Exp Bot. 2002 May;53(372):1351-65. J Exp Bot. 2002. PMID: 11997381 Review.
-
A 3D-printed hollow microneedle-based electrochemical sensing device for in situ plant health monitoring.Biosens Bioelectron. 2024 May 1;251:116131. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116131. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Biosens Bioelectron. 2024. PMID: 38367566
-
Phytoextraction of Pb and Cd by the Mediterranean saltbush (Atriplex halimus L.): metal uptake in relation to salinity.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2009 Nov;16(7):844-54. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0224-3. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2009. PMID: 19597858
-
Application of Visible/Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging with Machine Learning for High-Throughput Plant Heavy Metal Stress Phenotyping: A Review.Plant Phenomics. 2023 Nov 30;5:0124. doi: 10.34133/plantphenomics.0124. eCollection 2023. Plant Phenomics. 2023. PMID: 38239738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parallel, Continuous Monitoring and Quantification of Programmed Cell Death in Plant Tissue.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(23):e2400225. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400225. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38531063 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Machine Learning Assisted Biosensors in Point-of-Care-Testing For Clinical Decisions.ACS Sens. 2024 Sep 27;9(9):4495-4519. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c01582. Epub 2024 Aug 15. ACS Sens. 2024. PMID: 39145721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-on-a-chip: continuous, soilless electrochemical monitoring of salt uptake and tolerance among different genotypes of tomato.Sens Diagn. 2024 Apr 11;3(5):799-808. doi: 10.1039/d4sd00065j. eCollection 2024 May 16. Sens Diagn. 2024. PMID: 38766392 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-powered activatable NIR-II fluorescent nanosensor for in vivo monitoring of plant stress responses.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 2;16(1):5114. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60182-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40456715 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal electronic-tattoo for plant immune response monitoring.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 4;16(1):3244. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58584-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40185801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Felle H. H., Waller F., Molitor A., Kogel K.-H., The mycorrhiza fungus Piriformospora indica induces fast root-surface pH signaling and primes systemic alkalinization of the leaf apoplast upon powdery mildew infection. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 22, 1179–1185 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Sirault X. R. R., James R. A., Furbank R. T., A new screening method for osmotic component of salinity tolerance in cereals using infrared thermography. Funct. Plant Biol. 36, 970–977 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Fujimaki S., Maruyama T., Suzui N., Kawachi N., Miwa E., Higuchi K., Base to tip and long-distance transport of sodium in the root of common reed [Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud.] at steady state under constant high-salt conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 56, 943–950 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

