TGF-βR2 signaling coordinates pulmonary vascular repair after viral injury in mice and human tissue
- PMID: 38295183
- PMCID: PMC12067352
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg6229
TGF-βR2 signaling coordinates pulmonary vascular repair after viral injury in mice and human tissue
Abstract
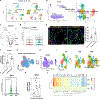
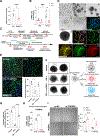
Disruption of pulmonary vascular homeostasis is a central feature of viral pneumonia, wherein endothelial cell (EC) death and subsequent angiogenic responses are critical determinants of the outcome of severe lung injury. A more granular understanding of the fundamental mechanisms driving reconstitution of lung endothelium is necessary to facilitate therapeutic vascular repair. Here, we demonstrated that TGF-β signaling through TGF-βR2 (transforming growth factor-β receptor 2) is activated in pulmonary ECs upon influenza infection, and mice deficient in endothelial Tgfbr2 exhibited prolonged injury and diminished vascular repair. Loss of endothelial Tgfbr2 prevented autocrine Vegfa (vascular endothelial growth factor α) expression, reduced endothelial proliferation, and impaired renewal of aerocytes thought to be critical for alveolar gas exchange. Angiogenic responses through TGF-βR2 were attributable to leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein 1, a proangiogenic factor that counterbalances canonical angiostatic TGF-β signaling. Further, we developed a lipid nanoparticle that targets the pulmonary endothelium, Lung-LNP (LuLNP). Delivery of Vegfa mRNA, a critical TGF-βR2 downstream effector, by LuLNPs improved the impaired regeneration phenotype of EC Tgfbr2 deficiency during influenza injury. These studies defined a role for TGF-βR2 in lung endothelial repair and demonstrated efficacy of an efficient and safe endothelial-targeted LNP capable of delivering therapeutic mRNA cargo for vascular repair in influenza infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Grasselli G, Tonetti T, Protti A, Langer T, Girardis M, Bellani G, Laffey J, Carrafiello G, Carsana L, Rizzuto C, Zanella A, Scaravilli V, Pizzilli G, Grieco DL, Di Meglio L, de Pascale G, Lanza E, Monteduro F, Zompatori M, Filippini C, Locatelli F, Cecconi M, Fumagalli R, Nava S, Vincent JL, Antonelli M, Slutsky AS, Pesenti A, Ranieri VM, on behalf of the collaborators, Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: A multicentre prospective observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 8, 1201–1208 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hsieh MJ, Lee WC, Cho HY, Wu MF, Hu HC, Kao KC, Chen NH, Tsai YH, Huang CC, Recovery of pulmonary functions, exercise capacity, and quality of life after pulmonary rehabilitation in survivors of ARDS due to severe influenza A (H1N1) pneumonitis. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 12, 643–648 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crapo JD, Barry BE, Gehr P, Bachofen M, Weibel ER, Cell number and cell characteristics of the normal human lung. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 126, 332–337 (1982). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

