Severe Hypoglycemia and Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia Persist in People With Type 1 Diabetes Despite Use of Diabetes Technology: Results From a Cross-sectional Survey
- PMID: 38295397
- PMCID: PMC11116910
- DOI: 10.2337/dc23-1765
Severe Hypoglycemia and Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia Persist in People With Type 1 Diabetes Despite Use of Diabetes Technology: Results From a Cross-sectional Survey
Abstract
Objective: To determine how diabetes technologies, including continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, impact glycemic metrics, prevalence of severe hypoglycemic events (SHEs), and impaired awareness of hypoglycemia (IAH) in people with type 1 diabetes in a real-world setting within the U.S.
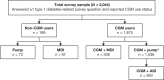
Research design and methods: In this retrospective, observational study with cross-sectional elements, participants aged ≥18 years were enrolled from the T1D Exchange Registry/online community. Participants completed a one-time online survey describing glycemic metrics, SHEs, and IAH. The primary objective was to determine the proportions of participants who reported achieving glycemic targets (assessed according to self-reported hemoglobin A1c) and had SHEs and/or IAH. We performed additional subgroup analyses focusing on the impact of CGM and insulin delivery modality.
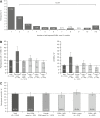
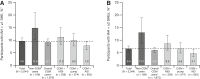
Results: A total of 2,074 individuals with type 1 diabetes were enrolled (mean ± SD age 43.0 ± 15.6 years and duration of type 1 diabetes 26.3 ± 15.3 years). The majority of participants (91.7%) were using CGM, with one-half (50.8%) incorporating AID. Despite high use of diabetes technologies, only 57.7% reported achieving glycemic targets (hemoglobin A1c <7%). SHEs and IAH still occurred, with ∼20% of respondents experiencing at least one SHE within the prior 12 months and 30.7% (95% CI 28.7, 32.7) reporting IAH, regardless of CGM or AID use.
Conclusions: Despite use of advanced diabetes technologies, a high proportion of people with type 1 diabetes do not achieve glycemic targets and continue to experience SHEs and IAH, suggesting an ongoing need for improved treatment strategies.
© 2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

Comment in
-
Automated Insulin Delivery: A Milestone on the Road to Insulin Independence in Type 1 Diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2024 Jun 1;47(6):918-920. doi: 10.2337/dci24-0007. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38768333 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gregory GA, Robinson TIG, Linklater SE, et al.; International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas Type 1 Diabetes in Adults Special Interest Group . Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022;10:741–760 - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association . Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45(Suppl. 1):S1–S2 - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Type 1 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG17], 2022. Accessed 24 August 2023. Available from https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng17
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

