Structure-activity relationship and target investigation of 2-aryl quinolines with nematocidal activity
- PMID: 38295619
- PMCID: PMC10845918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2024.100522
Structure-activity relationship and target investigation of 2-aryl quinolines with nematocidal activity
Abstract
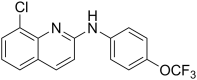
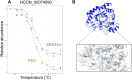
Within the context of our anthelmintic discovery program, we recently identified and evaluated a quinoline derivative, called ABX464 or obefazimod, as a nematocidal candidate; synthesised a series of analogues which were assessed for activity against the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans; and predicted compound-target relationships by thermal proteome profiling (TPP) and in silico docking. Here, we logically extended this work and critically evaluated the anthelmintic activity of ABX464 analogues on Haemonchus contortus (barber's pole worm) - a highly pathogenic nematode of ruminant livestock. First, we tested a series of 44 analogues on H. contortus (larvae and adults) to investigate the nematocidal pharmacophore of ABX464, and identified one compound with greater potency than the parent compound and showed moderate activity against a select number of other parasitic nematodes (including Ancylostoma, Heligmosomoides and Strongyloides species). Using TPP and in silico modelling studies, we predicted protein HCON_00074590 (a predicted aldo-keto reductase) as a target candidate for ABX464 in H. contortus. Future work aims to optimise this compound as a nematocidal candidate and investigate its pharmacokinetic properties. Overall, this study presents a first step toward the development of a new nematocide.
Keywords: Anthelmintics; Drug discovery; Haemonchus contortus; In silico docking; Target identification; Thermal proteome profiling.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Ang C.-S., Binos S., Knight M.I., Moate P.J., Cocks B.G., McDonagh M.B. Global survey of the bovine salivary proteome: integrating multidimensional prefractionation, targeted, and glycocapture strategies. J. Proteome Res. 2011;10:5059–5069. - PubMed
-
- Ashrafi K., Chang F.Y., Watts J.L., Fraser A.G., Kamath R.S., Ahringer J., Ruvkun G. Genome-wide RNAi analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans fat regulatory genes. Nature. 2003;421:268–272. - PubMed
-
- Bassetto C.C., Picharillo M.É., Newlands G.F.J., Smith W.D., Fernandes S., Siqueira E.R., Amarante A.F.T. Attempts to vaccinate ewes and their lambs against natural infection with Haemonchus contortus in a tropical environment. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014;44:1049–1054. - PubMed
-
- Becher I., Werner T., Doce C., Zaal E.A., Tögel I., Khan C.A., Rueger A., Muelbaier M., Salzer E., Berkers C.R., Fitzpatrick P.F., Bantscheff M., Savitski M.M. Thermal profiling reveals phenylalanine hydroxylase as an off-target of panobinostat. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016;12:908–910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

