Effect of vitamin B2, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E and folic acid in adults with essential hypertension: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 38296289
- PMCID: PMC10828875
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-074511
Effect of vitamin B2, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E and folic acid in adults with essential hypertension: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of the current study is to compare the treatment effects of different vitamins on essential hypertension to provide an initial basis for developing evidence-based practices.
Design: Systematic review and network meta-analysis.
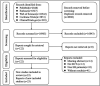
Data sources: Five electronic databases (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and ClinicalTrials.gov) were searched from their inception to 25 September 2023.
Outcomes: The primary outcomes were the difference between the intervention group and the control group in changes in office systolic blood pressure (SBP) and office diastolic blood pressure (DBP) from baseline. The secondary outcomes were the difference between the intervention group and the control group in changes in 24-hour mean ambulatory systolic blood pressure (24 hours SBP), 24-hour mean ambulatory diastolic blood pressure (24 hours DBP) and heart rate (HR) from baseline.
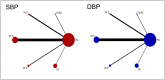
Results: A total of 23 studies comparing five vitamins (vitamin B2, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, folic acid) and involving 2218 participants were included. The included trials were all vitamin versus placebo, so the network was star-shaped. Among the five vitamins, only vitamin E was significantly more effective at reducing SBP (mean difference: -14.14 mm Hg, 95% credible intervals: -27.62 to -0.88) than placebo. In addition, no evidence was found that any of the five vitamins influenced DBP, 24 hours SBP, 24 hours DBP, or HR. The dose of vitamins, geographical region and percentage of males (only SBP) might be sources of heterogeneity. Sensitivity and subgroup analysis revealed that the effect of vitamin intervention on blood pressure varies according to different doses of vitamins.
Conclusions: According to the results, vitamin E might be an effective measure to reduce SBP, but more research is needed to validate this finding.
Prospero registration number: CRD42022352332.
Keywords: Blood Pressure; Hypertension; NUTRITION & DIETETICS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou B, Carrillo-Larco RM, Danaei G, et al. . Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021;398:957–80. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vamvakis A, Gkaliagkousi E, Lazaridis A, et al. . Impact of intensive lifestyle treatment (diet plus exercise) on endothelial and vascular function, arterial stiffness and blood pressure in stage 1 hypertension: results of the Hintreat randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2020;12:1326. 10.3390/nu12051326 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
