Acute Liver Injury and Bilateral Pulmonary Artery Thrombosis Due to Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
- PMID: 38296476
- PMCID: PMC11442920
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2989-23
Acute Liver Injury and Bilateral Pulmonary Artery Thrombosis Due to Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
Abstract
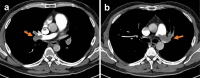
A 46-year-old Japanese man was referred to our hospital because of a marked increase in his eosinophil count (22,870/μL) and elevated liver enzyme levels. Computed tomography (CT) showed thrombi measuring approximately 8 cm in both femoral veins. A liver biopsy revealed eosinophilic infiltration, hepatocyte necrosis, fibrosis, and multiple thrombi. We suspected acute liver injury and deep vein thrombosis associated with hypereosinophilic syndrome and initiated steroids and heparin treatment. Four days after starting treatment, the patient experienced sudden chest pain and cardiopulmonary arrest. CT revealed bilateral pulmonary artery thrombosis, and despite administration of a tissue plasminogen activator, the patient died.
Keywords: acute liver injury; hypereosinophilic syndrome; pulmonary embolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Shomali W, Gotlib J. World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 97: 129-148, 2022. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Ed. In: Leukemia. The 5(th) Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Hematolymphoid Tumors. Exon Publications, Brisbane, 2022 [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 29]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.36255/exon-publications-leukemia. - PubMed
-
- Kawamura T, Hiraoka A, Toshimori A, et al. . A possible case of hepatitis due to hypereosinophilic syndrome. Intern Med 55: 1453-1458, 2016. - PubMed

