Molecular insights into the dynamic modulation of bacterial ClpP function and oligomerization by peptidomimetic boronate compounds
- PMID: 38296985
- PMCID: PMC10830462
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-51787-0
Molecular insights into the dynamic modulation of bacterial ClpP function and oligomerization by peptidomimetic boronate compounds
Abstract
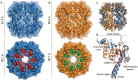
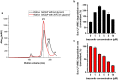
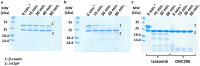
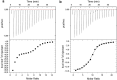
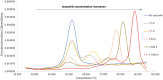
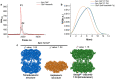
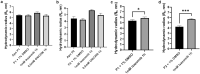
Bacterial caseinolytic protease P subunit (ClpP) is important and vital for cell survival and infectivity. Recent publications describe and discuss the complex structure-function relationship of ClpP and its processive activity mediated by 14 catalytic sites. Even so, there are several aspects yet to be further elucidated, such as the paradoxical allosteric modulation of ClpP by peptidomimetic boronates. These compounds bind to all catalytic sites, and in specific conditions, they stimulate a dysregulated degradation of peptides and globular proteins, instead of inhibiting the enzymatic activity, as expected for serine proteases in general. Aiming to explore and explain this paradoxical effect, we solved and refined the crystal structure of native ClpP from Staphylococcus epidermidis (Se), an opportunistic pathogen involved in nosocomial infections, as well as ClpP in complex with ixazomib at 1.90 Å and 2.33 Å resolution, respectively. The interpretation of the crystal structures, in combination with complementary biochemical and biophysical data, shed light on how ixazomib affects the ClpP conformational state and activity. Moreover, SEC-SAXS and DLS measurements show, for the first time, that a peptidomimetic boronate compound also induces the assembly of the tetradecameric structure from isolated homomeric heptameric rings of a gram-positive organism.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

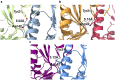
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

