Infected erythrocytes and plasma proteomics reveal a specific protein signature of severe malaria
- PMID: 38297098
- PMCID: PMC10897182
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-023-00010-0
Infected erythrocytes and plasma proteomics reveal a specific protein signature of severe malaria
Abstract
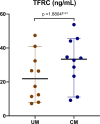
Cerebral malaria (CM), the most lethal complication of Plasmodium falciparum severe malaria (SM), remains fatal for 15-25% of affected children despite the availability of treatment. P. falciparum infects and multiplies in erythrocytes, contributing to anemia, parasite sequestration, and inflammation. An unbiased proteomic assessment of infected erythrocytes and plasma samples from 24 Beninese children was performed to study the complex mechanisms underlying CM. A significant down-regulation of proteins from the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and an up-regulation of the erythroid precursor marker transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC) were associated with infected erythrocytes from CM patients. At the plasma level, the samples clustered according to clinical presentation. Significantly, increased levels of the 20S proteasome components were associated with SM. Targeted quantification assays confirmed these findings on a larger cohort (n = 340). These findings suggest that parasites causing CM preferentially infect reticulocytes or erythroblasts and alter their maturation. Importantly, the host plasma proteome serves as a specific signature of SM and presents a remarkable opportunity for developing innovative diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cerebral Malaria; LC-MS/MS; Plasmodium falciparum; Red Blood Cells.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Andrade CM, Fleckenstein H, Thomson-Luque R, Doumbo S, Lima NF, Anderson C, Hibbert J, Hopp CS, Tran TM, Li S, et al. Increased circulation time of Plasmodium falciparum underlies persistent asymptomatic infection in the dry season. Nat Med. 2020;26:1929–1940. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1084-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aschemeyer S, Qiao B, Stefanova D, Valore EV, Sek AC, Ruwe TA, Vieth KR, Jung G, Casu C, Rivella S, et al. Structure-function analysis of ferroportin defines the binding site and an alternative mechanism of action of hepcidin. Blood. 2018;131:899–910. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-05-786590. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

