Purification and characterization of L-arginine deiminase from Penicillium chrysogenum
- PMID: 38297214
- PMCID: PMC10829382
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-024-03192-w
Purification and characterization of L-arginine deiminase from Penicillium chrysogenum
Abstract
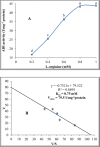
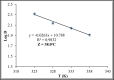
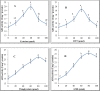
L-arginine deiminase (ADI, EC 3.5.3.6) hydrolyzes arginine to ammonia and citrulline which is a natural supplement in health care. ADI was purified from Penicillium chrysogenum using 85% ammonium sulfate, DEAE-cellulose and Sephadex G200. ADI was purified 17.2-fold and 4.6% yield with a specific activity of 50 Umg- 1 protein. The molecular weight was 49 kDa. ADI expressed maximum activity at 40oC and an optimum pH of 6.0. ADI thermostability was investigated and the values of both t0.5 and D were determined. Kd increased by temperature and the Z value was 38oC. ATP, ADP and AMP activated ADI up to 0.6 mM. Cysteine and dithiothreitol activated ADI up to 60 µmol whereas the activation by thioglycolate and reduced glutathione (GSH) prolonged to 80 µmol. EDTA, α,α-dipyridyl, and o-phenanthroline inactivated ADI indicating that ADI is a metalloenzyme. N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), butanedione (BD), dansyl chloride (DC), diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) and N-acetyl-imidazole (NAI) inhibited ADI activity indicating the necessity of sulfhydryl, tryptophanyl, arginyl, lysyl, histidyl and tyrosyl groups, respectively for ADI catalysis. The obtained results show that ADI from P. chrysogenum could be a potential candidate for industrial and biotechnological applications.
Keywords: Activation; Active groups; Arginine deiminase; Kinetics; P.chrysogenum; Purification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Van Beek JH, Supandi F, Gavai AK, de Graaf AA, Binsl TW, Hettling H. Simulating the physiology of athletes during endurance sports events: Modelling human energy conversion and metabolism. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Pqhysical and Engineering Sciences. 2011; 369(1954): 4295–4315. 10.1098/rsta.2011.0166. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kassab M. Identification and molecular characterization of arginine deiminase-producing bacteria in Egyptian soil from various soil environments. J Med Life Sci. 2023;5(1):43–75. doi: 10.21608/jmals.2023.295732. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

