Antagonistic effectiveness of Anacardium occidentale leaf extract on lead-acetate exposure-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats
- PMID: 38298047
- PMCID: PMC10834079
- DOI: 10.5620/eaht.2023028
Antagonistic effectiveness of Anacardium occidentale leaf extract on lead-acetate exposure-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats
Abstract
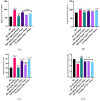
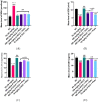
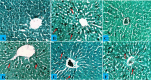
Lead (Pb) poisoning is an environmental substance that accumulates in the hepato-renal tissue, which is hazardous to health, while Anacardium occidentale L. is a tropical herb used to treat oxidative stress and inflammatory diseases. The aim of this study was to investigate the antagonistic effect of Anacardium occidentale leaf extract on lead acetate exposure-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats. Thirty-six adult Wistar rats were split into six equal groups (n = 6). Group I served as a control, and groups II and III were administered lead acetate (50 mg/kg) and Anacardium occidentale leaf extract (400 mg/kg), respectively, while rats in groups IV-VI were administered Anacardium occidentale (L) extract (200 mg/kg and 400 mg/kg) and 10 mg/kg of Succimer, respectively, and were then administered lead acetate (50 mg/kg). When compared to the group I, rats administered lead acetate showed an increase in hepatic enzymes, urea, creatinine, MDA, TNF-α, and IL-1β (p < 0.001) levels and decreased levels of SOD, CAT, and GSH, whereas Anacardium occidentale prevented the increase in hepatorenal function parameters, oxidative stress, and inflammatory markers (TNF-α and IL-1β) induced by lead acetate. Rats administered only lead acetate had a marked increase in hepatic Pb concentration, severe hepatic steatosis, and renal glomerulus degeneration. However, treatment with Anacardium occidentale extract and succimer decreases the Pb concentration, oxidative stress, and inflammation, and also reduces histological liver steatosis and glomerular cytoarchitecture deterioration in the kidney. The results of this study revealed that Anacardium occidentale extract protects against lead acetate-induced liver and kidney toxicity by decreasing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Keywords: Anacardium occidentale; Kidney; Lead acetate; Liver; Oxidative stress; Succimer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
The research was approved by University of Maiduguri Directorate of Academic Planning and Monitoring (Approval No: (UM/HA/UGR20.21-0740067) and was conducted according to the ARRIVE Guidelines.
Figures




References
-
- Mudipalli A. Lead hepatotoxicity & potential health effects. Indian J Med Res. 2007;126(6):518–527. - PubMed
-
- Al-Megrin WA, Alkhuriji AF, Yousef AOS, Metwally DM, Habotta OA, Kassab RB, et al. Antagonistic efficacy of luteolin against lead acetate exposure-associated with hepatotoxicity is mediated via antioxidant, anti-Inflammatory, and antiapoptotic activities. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019;9(1):10. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

