Formulation of precise exercise intervention strategy for adolescent depression
- PMID: 38298170
- PMCID: PMC10990816
- DOI: 10.1002/pchj.726
Formulation of precise exercise intervention strategy for adolescent depression
Abstract
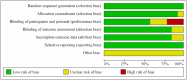
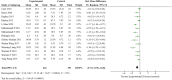
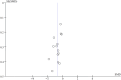
The high incidence of adolescent depression has become the focus of social and academic attention. Exercise is an important method to improve adolescent depression, but its intervention effect is still controversial. This study first compares and analyzes the relevant studies at home and abroad and finds that exercise prescription in adolescent depression intervention is not accurate enough. A meta-analysis was conducted to develop a precise exercise intervention strategy for adolescent depression. Firstly, this thesis identified how to optimize five elements (exercise intensity, exercise frequency, exercise time, exercise cycle, and exercise type) of exercise prescription to improve depression in adolescents. This is the problem. Furthermore, the concept of "precision exercise" was proposed, and a precision exercise intervention strategy (moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for 8-10 weeks, 3 times/week, 45-50 min/time) was constructed to improve adolescent depression. This paper also presents research that strengthens the cross-sectional research and empirical research on adolescent depression and establishes a precision exercise prescription database for adolescent depression in China. In conclusion, this study not only puts forward the concept of "precision exercise" but also constructs a precision exercise intervention strategy for adolescent depression, which has important theoretical and practical significance for improving the high incidence of adolescent depression.
Keywords: depression; mental health; precise exercise; teenagers.
© 2024 The Authors. PsyCh Journal published by Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
-
Pilot aerobic exercise intervention for youth at-risk for serious mental illness.Early Interv Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;15(3):547-553. doi: 10.1111/eip.12977. Epub 2020 May 26. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 32452641
-
The strategies of exercise intervention for adolescent depression: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 4;13:974382. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.974382. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36687827 Free PMC article.
-
Treating depression with physical activity in adolescents and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Psychol Med. 2018 May;48(7):1068-1083. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717002653. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Psychol Med. 2018. PMID: 28994355
-
Clinician perspectives and practices regarding the use of exercise in the treatment of adolescent depression.J Sports Sci. 2018 Jun;36(12):1371-1377. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2017.1383622. Epub 2017 Sep 25. J Sports Sci. 2018. PMID: 28945524
References
-
- Abbas, J. , Aman, J. , Nurunnabi, M. , & Bano, S. (2019). The impact of social media on learning behavior for sustainable education: Evidence of students from selected universities in Pakistan. Sustainability, 11(6), 1683. 10.3390/su11061683 - DOI
-
- Al‐Halbusi, H. , Al‐Sulaiti, K. , Abbas, J. , & Al‐Sulaiti, I. (2022). Assessing factors influencing technology adoption for online purchasing amid COVID‐19 in Qatar: Moderating role of word of mouth. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 942527. 10.3389/fenvs.2022.942527 - DOI
-
- Aqeel, M. , Abbas, J. , Shuja, K. H. , Rehna, T. , Ziapour, A. , Yousaf, I. , & Karamat, T. (2022). The influence of illness perception, anxiety and depression disorders on students mental health during COVID‐19 outbreak in Pakistan: A web‐based cross‐sectional survey. International Journal of Human Rights in Healthcare, 15(1), 17–30. 10.1108/IJHRH-10-2020-0095 - DOI
-
- Azadi, N. A. , Ziapour, A. , Lebni, J. Y. , Irandoost, S. F. , Abbas, J. , & Chaboksavar, F. (2021). The effect of education based on health belief model on promoting preventive behaviors of hypertensive disease in staff of the Iran University of Medical Sciences. Archives of Public Health, 79(1), 69. 10.1186/s13690-021-00594-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

