Lung Ultrasound Assessment of Lung Hyperinflation in Patients with Stable COPD: An Effective Diagnostic Tool
- PMID: 38298918
- PMCID: PMC10829508
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S441374
Lung Ultrasound Assessment of Lung Hyperinflation in Patients with Stable COPD: An Effective Diagnostic Tool
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the degree of lung hyperinflation (LH) in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by lung ultrasound score (LUS) and assess its value.
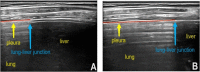
Patients and methods: We conducted a study of 149 patients with stable COPD and 100 healthy controls recruited by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University. The pleural sliding displacement (PSD) was measured, the sliding of the pleura in different areas was observed, and LUS was calculated from both of them. The diaphragm excursion (DE), residual capacity (RV), total lung capacity (TLC), inspiratory capacity (IC) and functional residual capacity (FRC) were measured. We described the correlation between ultrasound indicators and pulmonary function indicators reflecting LH. Multiple linear regression analysis was used. The ROC curves of LUS and DE were drawn to evaluate their diagnostic efficacy, and De Long method was used for comparison.
Results: (1) The LUS of patients with stable COPD were positively correlated with RV, TLC, RV/TLC and FRC and negatively correlated with IC and IC/TLC (r1=0.72, r2=0.41, r3=0.72, r4=0.70, r5=-0.56, r6=-0.65, P < 0.001). The correlation was stronger than that between DE at maximal deep inspiration and the corresponding pulmonary function indices (r1=-0.41, r2=-0.26, r3=-0.40, r4=-0.43, r5=0.30, r6=0.37, P < 0.001). (2) Multiple linear regression analysis showed that LUS were significantly correlated with IC/TLC and RV/TLC. (3) With IC/TLC<25% and RV/TLC>60% as the diagnostic criterion of severe LH, the areas under the ROC curves of LUS and DE at maximal deep inspiration for diagnosing severe LH were 0.914 and 0.385, 0.845 and 0.543, respectively (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The lung ultrasound score is an important parameter for evaluating LH. LUS is better than DE at maximal deep inspiration for diagnosing severe LH and is expected to become an effective auxiliary tool for evaluating LH.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; lung hyperinflation; pleural sliding displacement; pulmonary function; ultrasound.
© 2024 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

