Macleaya cordata isoquinoline alkaloids attenuate Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal epithelium injury in broiler chickens by co-regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways
- PMID: 38299145
- PMCID: PMC10828024
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1335359
Macleaya cordata isoquinoline alkaloids attenuate Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal epithelium injury in broiler chickens by co-regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways
Abstract
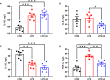
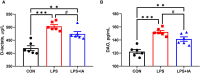
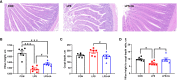
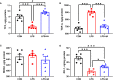
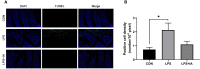
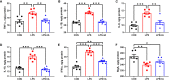
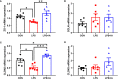
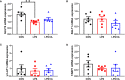
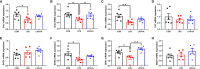
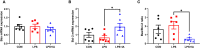
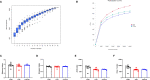
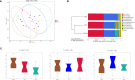
This study sought to explore the effects and potential mechanisms of dietary supplementation with isoquinoline alkaloids (IA) from Macleaya cordata to alleviate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced intestinal epithelium injury in broilers. A total of 486 1-day-old broilers were assigned at random to a control (CON) group, LPS group, and LPS+IA group in a 21-d study. The CON and LPS groups received a basal diet, while the LPS+IA group received a basal diet supplemented with 0.6 mg/kg IA. At 17, 19, and 21 days of age, the LPS and LPS+BP groups were injected intraperitoneally with LPS, and the CON group was intraperitoneally injected equivalent amount of saline solution. The results manifested that LPS injection caused intestinal inflammation and lipid peroxidation, disrupted intestinal barrier and function, and increased the abundance of harmful microorganisms. However, dietary IA supplementation alleviated LPS-induced adverse changes in intestinal morphology, apoptosis, mucosal barrier integrity, cecum microorganisms, and homeostasis disorder by decreasing inflammatory cytokines and enhancing antioxidant-related genes expressions; inhibited LPS-induced increases in TLR4 and NF-κB expressions and decreases in Nrf2 and GPX1 genes expressions. Our findings indicated that Macleaya cordata IA addition attenuated LPS-induced intestinal epithelium injury and disorder of intestinal homeostasis by enhancing the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacity of broiler chickens possibly via co-regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways.
Keywords: Macleaya cordata isoquinoline alkaloid; broiler; intestinal epithelium injury; intestinal inflammation; lipopolysaccharide; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Han, Liu, Jia, Comer, Wang, Pan, Zhao, Jiang, Jiao, Huang, Yang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective effect of Macleaya cordata isoquinoline alkaloids on lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in broilers.Anim Biosci. 2024 Jan;37(1):131-141. doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0267. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Anim Biosci. 2024. PMID: 37946426 Free PMC article.
-
Artemisia ordosica Polysaccharide Alleviated Lipopolysaccharide-induced Oxidative Stress of Broilers via Nrf2/Keap1 and TLR4/NF-κB Pathway.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Oct 15;223:112566. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112566. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 34340153
-
Music intervention mitigates LPS-induced gut barrier disruption and immune stress in broilers via TLR4/NF-κB regulation.Poult Sci. 2025 Jul;104(7):105189. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105189. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40294553 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus coagulans TL3 Inhibits LPS-Induced Caecum Damage in Rat by Regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Nrf2 Signal Pathways and Modulating Intestinal Microflora.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 7;2022:5463290. doi: 10.1155/2022/5463290. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35178157 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation with farnesol confers a protective effect on the intestine of broiler chickens challenged with lipopolysaccharide by reshaping intestinal flora structure and regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104942. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104942. Epub 2025 Feb 23. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40010048 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of dietary formic acid polymer supplementation on growth performance, blood parameters, and intestinal health in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 21;16:1587832. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1587832. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40469718 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of isoquinoline alkaloids as an alternative to antibiotic on oxidative stress, inflammatory status, and cecal microbiome of broilers under high stocking density.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104671. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104671. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39689480 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens TL promotes gut health of broilers by the contribution of bacterial extracellular polysaccharides through its anti-inflammatory potential.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 23;15:1455996. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1455996. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39376562 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviating effects of dietary formic acid polymer supplementation on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury in gut-liver axis of broilers.Poult Sci. 2025 Feb;104(2):104698. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104698. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39721259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Celi P, Cowiesonb AJ, Fru-Nji F, Steinert RE, Kluenterb AM, Verlhacd V. Gastrointestinal functionality in animal nutrition and health: New opportunities for sustainable animal production. Anim Feed Sci Tech (2017) 234:88–100. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.09.012 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

