The Role of Psychopathology and Emotion Regulation in the Intergenerational Transmission of Childhood Abuse: A Family Study
- PMID: 38299462
- PMCID: PMC11656633
- DOI: 10.1177/10775595231223657
The Role of Psychopathology and Emotion Regulation in the Intergenerational Transmission of Childhood Abuse: A Family Study
Abstract
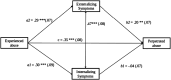
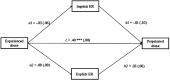
Previous studies have shown that parents with a history of childhood abuse are at increased risk of perpetrating child abuse. To break the cycle of childhood abuse we need to better understand the mechanisms that play a role. In a cross-sectional extended family design including three generations (N = 250, 59% female), we examined the possible mediating role of parental psychopathology and emotion regulation in the association between a history of childhood abuse and perpetrating child abuse. Parents' own history of childhood abuse was associated with perpetrating abuse toward their children, and externalizing (but not internalizing) problems partially mediated this association statistically. Implicit and explicit emotion regulation were not associated with experienced or perpetrated abuse. Findings did not differ across fathers and mothers. Findings underline the importance of (early) treatment of externalizing problems in parents with a history of childhood abuse, to possibly prevent the transmission of child abuse.
Keywords: abuse; emotion regulation; externalizing problems; intergenerational transmission; psychopathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intergenerational effects of childhood maltreatment: A systematic review of the parenting practices of adult survivors of childhood abuse, neglect, and violence.Clin Psychol Rev. 2020 Aug;80:101891. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101891. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Clin Psychol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32745835 Free PMC article.
-
Intergenerational transmission of child maltreatment: Predictors of child emotional maltreatment among 11 to 17 years old children residing in communities of Karachi, Pakistan.Child Abuse Negl. 2019 May;91:109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Child Abuse Negl. 2019. PMID: 30856598
-
Childhood Emotional and Conduct Problems in Childhood and Adolescence Differentially Associated with Intergenerational Maltreatment Continuity and Parental Internalizing Symptoms.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2020 Jan;48(1):29-42. doi: 10.1007/s10802-019-00575-w. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31313061
-
Gender-specific linkages of parents' childhood physical abuse and neglect with children's problem behaviour: evidence from Japan.BMC Public Health. 2016 May 14;16:403. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3072-3. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27179941 Free PMC article.
-
The intergenerational transmission of child maltreatment: A three-level meta-analysis.Child Abuse Negl. 2018 Oct;84:131-145. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2018.07.037. Epub 2018 Aug 4. Child Abuse Negl. 2018. PMID: 30086419 Review.
References
-
- Achenbach T. M., Dumenci L., Rescorla L. A. (2003). DSM-oriented and empirically based approaches to constructing scales from the same item pools. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology: The Official Journal for the Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, American Psychological Association, Division 53, 32(3), 328–340. 10.1207/S15374424JCCP3203_02 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Achenbach T. M., Ivanova M. Y., Rescorla L. A., Turner L. V., Althoff R. R. (2016). Internalizing/externalizing problems: Review and recommendations for clinical and research applications. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 55(8), 647–656. 10.1016/j.jaac.2016.05.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alink L., Cyr C., Madigan S. (2019). The effect of maltreatment experiences on maltreating and dysfunctional parenting: A search for mechanisms. Development and Psychopathology, 31(1), 1–7. 10.1017/s0954579418001517 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

