Ceramides are fuel gauges on the drive to cardiometabolic disease
- PMID: 38300524
- PMCID: PMC11381030
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00008.2023
Ceramides are fuel gauges on the drive to cardiometabolic disease
Abstract
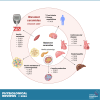
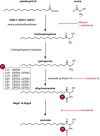
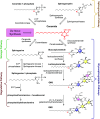
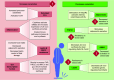
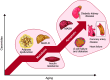
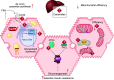
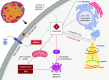
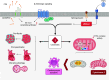
Ceramides are signals of fatty acid excess that accumulate when a cell's energetic needs have been met and its nutrient storage has reached capacity. As these sphingolipids accrue, they alter the metabolism and survival of cells throughout the body including in the heart, liver, blood vessels, skeletal muscle, brain, and kidney. These ceramide actions elicit the tissue dysfunction that underlies cardiometabolic diseases such as diabetes, coronary artery disease, metabolic-associated steatohepatitis, and heart failure. Here, we review the biosynthesis and degradation pathways that maintain ceramide levels in normal physiology and discuss how the loss of ceramide homeostasis drives cardiometabolic pathologies. We highlight signaling nodes that sense small changes in ceramides and in turn reprogram cellular metabolism and stimulate apoptosis. Finally, we evaluate the emerging therapeutic utility of these unique lipids as biomarkers that forecast disease risk and as targets of ceramide-lowering interventions that ameliorate disease.
Keywords: ceramides; diabetes; lipotoxicity; metabolic disease; sphingolipids.
Conflict of interest statement
S.A.S. is a consultant, cofounder, and shareholder in Centaurus Therapeutics, LLC. None of the other authors has any conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Llorca-Colomer F, Murillo-Llorente MT, Legidos-Garcia ME, Palau-Ferre A, Pérez-Bermejo M. Differences in classification standards for the prevalence of overweight and obesity in children. a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Epidemiol 14: 1031–1052, 2022. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S375981. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holland WL, Miller RA, Wang ZV, Sun K, Barth BM, Bui HH, Davis KE, Bikman BT, Halberg N, Rutkowski JM, Wade MR, Tenorio VM, Kuo MS, Brozinick JT, Zhang BB, Birnbaum MJ, Summers SA, Scherer PE. Receptor-mediated activation of ceramidase activity initiates the pleiotropic actions of adiponectin. Nat Med 17: 55–63, 2011. doi: 10.1038/nm.2277. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holland WL, Bikman BT, Wang LP, Yuguang G, Sargent KM, Bulchand S, Knotts TA, Shui G, Clegg DJ, Wenk MR, Pagliassotti MJ, Scherer PE, Summers SA. Lipid-induced insulin resistance mediated by the proinflammatory receptor TLR4 requires saturated fatty acid-induced ceramide biosynthesis in mice. J Clin Invest 121: 1858–1870, 2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI43378. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

