Deep Learning Detection of Early Retinal Peripheral Degeneration From Ultra-Widefield Fundus Photographs of Asymptomatic Young Adult (17-19 Years) Candidates to Airforce Cadets
- PMID: 38300623
- PMCID: PMC10851781
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.13.2.1
Deep Learning Detection of Early Retinal Peripheral Degeneration From Ultra-Widefield Fundus Photographs of Asymptomatic Young Adult (17-19 Years) Candidates to Airforce Cadets
Abstract
Purpose: Artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted ultra-widefield (UWF) fundus photographic interpretation is beneficial to improve the screening of fundus abnormalities. Therefore we constructed an AI machine-learning approach and performed preliminary training and validation.
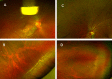
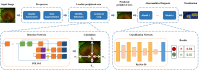
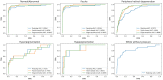
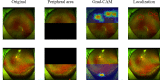
Methods: We proposed a two-stage deep learning-based framework to detect early retinal peripheral degeneration using UWF images from the Chinese Air Force cadets' medical selection between February 2016 and June 2022. We developed a detection model for the localization of optic disc and macula, which are used to find the peripheral areas. Then we developed six classification models for the screening of various retinal cases. We also compared our proposed framework with two baseline models reported in the literature. The performance of the screening models was evaluated by area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) with 95% confidence interval.
Results: A total of 3911 UWF fundus images were used to develop the deep learning model. The external validation included 760 UWF fundus images. The results of comparison study revealed that our proposed framework achieved competitive performance compared to existing baselines while also demonstrating significantly faster inference time. The developed classification models achieved an average AUC of 0.879 on six different retinal cases in the external validation dataset.
Conclusions: Our two-stage deep learning-based framework improved the machine learning efficiency of the AI model for fundus images with high resolution and many interference factors by maximizing the retention of valid information and compressing the image file size.
Translational relevance: This machine learning model may become a new paradigm for developing UWF fundus photography AI-assisted diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Performance of Ultra-Widefield Fundus Imaging for Screening Retinal Lesions in Rural Locales.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023 Nov 1;141(11):1045-1051. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.4650. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37856107 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Early Detection of Retinitis Pigmentosa - the Most Common Inherited Retinal Degeneration.J Digit Imaging. 2021 Aug;34(4):948-958. doi: 10.1007/s10278-021-00479-6. Epub 2021 Jul 9. J Digit Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34244880 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection of retinal exudates and drusen in ultra-widefield fundus images based on deep learning.Eye (Lond). 2022 Aug;36(8):1681-1686. doi: 10.1038/s41433-021-01715-7. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Eye (Lond). 2022. PMID: 34345030 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-Widefield Imaging for Evaluation of the Myopic Eye.Semin Ophthalmol. 2021 May 19;36(4):185-190. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2021.1887904. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Semin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33620294 Review.
-
Performance of deep learning for detection of chronic kidney disease from retinal fundus photographs: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2024 Mar;34(2):502-509. doi: 10.1177/11206721231199848. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37671422
Cited by
-
Discriminative, generative artificial intelligence, and foundation models in retina imaging.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2024 Nov 28;14(4):473-485. doi: 10.4103/tjo.TJO-D-24-00064. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39803410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of multimodal imaging in the clinical diagnosis of inherited retinal degenerations.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2024 Dec 3;14(4):486-496. doi: 10.4103/tjo.TJO-D-24-00066. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39803408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultra-wide-field fundus photography and AI-based screening and referral for multiple ocular fundus diseases.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Jun 17;6(6):102187. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102187. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 40499544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silva PS, Cavallerano JD, Sun JK, et al. .. Nonmydriatic ultrawide field retinal imaging compared with dilated standard 7-field 35-mm photography and retinal specialist examination for evaluation of diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012; 154(3): 549–559.e2. - PubMed
-
- Nagiel A, Lalane RA, Sadda SR, et al. .. Ultra-widefield fundus imaging: a review of clinical applications and future trends. Retina. 2016; 36: 660–678. - PubMed
-
- Wu T, Qi L, Tang Y, Lyu S, He J, Liu Y. Peripheral retinal abnormalities in adolescents with normal vision in Air Force cadets’ recruitment: a cross sectional study. Acad J Chin PLA Med Sch. 2022; 43(6): 5.
-
- Flaxel CJ, Adelman RA, Bailey ST, et al. .. Posterior vitreous detachment, retinal breaks, and lattice degeneration preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2020; 127(1): P146–P181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

