Small Molecule Antagonists of the DNA Repair ERCC1/XPA Protein-Protein Interaction
- PMID: 38300970
- PMCID: PMC11031295
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202300648
Small Molecule Antagonists of the DNA Repair ERCC1/XPA Protein-Protein Interaction
Abstract
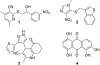
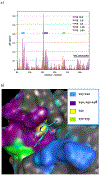
The DNA excision repair protein ERCC1 and the DNA damage sensor protein, XPA are highly overexpressed in patient samples of cisplatin-resistant solid tumors including lung, bladder, ovarian, and testicular cancer. The repair of cisplatin-DNA crosslinks is dependent upon nucleotide excision repair (NER) that is modulated by protein-protein binding interactions of ERCC1, the endonuclease, XPF, and XPA. Thus, inhibition of their function is a potential therapeutic strategy for the selective sensitization of tumors to DNA-damaging platinum-based cancer therapy. Here, we report on new small-molecule antagonists of the ERCC1/XPA protein-protein interaction (PPI) discovered using a high-throughput competitive fluorescence polarization binding assay. We discovered a unique structural class of thiopyridine-3-carbonitrile PPI antagonists that block a truncated XPA polypeptide from binding to ERCC1. Preliminary hit-to-lead studies from compound 1 reveal structure-activity relationships (SAR) and identify lead compound 27 o with an EC50 of 4.7 μM. Furthermore, chemical shift perturbation mapping by NMR confirms that 1 binds within the same site as the truncated XPA67-80 peptide. These novel ERCC1 antagonists are useful chemical biology tools for investigating DNA damage repair pathways and provide a good starting point for medicinal chemistry optimization as therapeutics for sensitizing tumors to DNA damaging agents and overcoming resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy.
Keywords: DNA damage and repair, cisplatin, chemotherapy; ERCC1, XPA, XPF; NMR structure; high-throughput screening (HTS); nucleotide excision repair (NER); protein-protein interaction (PPI); small molecule inhibitor.
© 2024 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Figures

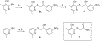



References
-
- Martin LP; Hamilton TC; Schilder RJ, Platinum resistance: The role of DNA repair pathways. Clinical Cancer Research 2008, 14 (5), 1291–1295. - PubMed
-
- Groelly FJ; Fawkes M; Dagg RA; Blackford AN; Tarsounas M Targeting DNA damage response pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2023, 23 (2), 78–94. DOI: 10.1038/s41568-022-00535-5; - DOI - PubMed
- McPherson KS; Korzhnev DM Targeting protein-protein interactions in the DNA damage response pathways for cancer chemotherapy. RSC Chem Biol 2021, 2 (4), 1167–1195. DOI: 10.1039/d1cb00101a; (c) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang Y; Duan M; Peng Z; Fan R; He Y; Zhang H; Xiong W; Jiang W Advances of DNA Damage Repair-Related Drugs and Combination With Immunotherapy in Tumor Treatment. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 854730. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.854730; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Powell SN; Bindra RS, Targeting the DNA damage response for cancer therapy. DNA Repair (Amst) 2009, 8 (9), 1153–65; - PubMed
- Jiang M; Jia K; Wang L; Li W; Chen B; Liu Y; Wang H; Zhao S; He Y; Zhou C Alterations of DNA damage response pathway: Biomarker and therapeutic strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 2021, 11 (10), 2983–2994. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Houtsmuller AB; Rademakers S; Nigg AL; Hoogstraten D; Hoeijmakers JH; Vermeulen W, Action of DNA repair endonuclease ERCC1/XPF in living cells. Science 1999, 284 (5416), 958–61; - PubMed
- Scharer OD ERCC1-XPF endonuclease-positioned to cut. EMBO J 2017, 36 (14), 1993–1995. DOI: 10.15252/embj.201797489. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borszekova Pulzova L; Ward TA; Chovanec M XPA: DNA Repair Protein of Significant Clinical Importance. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21 (6); - PMC - PubMed
- Krasikova YS; Lavrik OI; Rechkunova NI The XPA Protein-Life under Precise Control. Cells 2022, 11 (23). DOI: 10.3390/cells11233723; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Park CJ; Choi BS, The protein shuffle - Sequential interactions among components of the human nucleotide excision repair pathway. Febs Journal 2006, 273 (8), 1600–1608; - PubMed
- Li L; Elledge SJ; Peterson CA; Bales ES; Legerski RJ, SPECIFIC ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE HUMAN DNA-REPAIR PROTEINS XPA AND ERCC1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1994, 91 (11), 5012–5016; - PMC - PubMed
- Sugitani N; Sivley RM; Perry KE; Capra JA; Chazin WJ XPA: A key scaffold for human nucleotide excision repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 2016, 44, 123–135. DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

