Patient-Reported Outcomes in OlympiA: A Phase III, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Adjuvant Olaparib in g BRCA1/2 Mutations and High-Risk Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Early Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38301187
- PMCID: PMC11095886
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.01214
Patient-Reported Outcomes in OlympiA: A Phase III, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Adjuvant Olaparib in g BRCA1/2 Mutations and High-Risk Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Early Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The OlympiA randomized phase III trial compared 1 year of olaparib (OL) or placebo (PL) as adjuvant therapy in patients with germline BRCA1/2, high-risk human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early breast cancer after completing (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy ([N]ACT), surgery, and radiotherapy. The patient-reported outcome primary hypothesis was that OL-treated patients may experience greater fatigue during treatment.
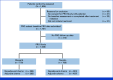
Methods: Data were collected before random assignment, and at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months. The primary end point was fatigue, measured with the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue scale. Secondary end points, assessed with the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire, Core 30 item, included nausea and vomiting (NV), diarrhea, and multiple functional domains. Scores were compared between treatment groups using mixed model for repeated measures. Two-sided P values <.05 were statistically significant for the primary end point. All secondary end points were descriptive.
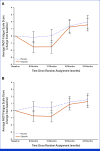
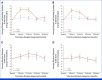
Results: One thousand five hundred and thirty-eight patients (NACT: 746, ACT: 792) contributed to the analysis. Fatigue severity was statistically significantly greater for OL versus PL, but not clinically meaningfully different by prespecified criteria (≥3 points) at 6 months (diff OL v PL: NACT: -1.3 [95% CI, -2.4 to -0.2]; P = .022; ACT: -1.3 [95% CI, -2.3 to -0.2]; P = .017) and 12 months (NACT: -1.6 [95% CI, -2.8 to -0.3]; P = .017; ACT: -1.3 [95% CI, -2.4 to -0.2]; P = .025). There were no significant differences in fatigue severity between treatment groups at 18 and 24 months. NV severity was worse in patients treated with OL compared with PL at 6 months (NACT: 6.0 [95% CI, 4.1 to 8.0]; ACT: 5.3 [95% CI, 3.4 to 7.2]) and 12 months (NACT: 6.4 [95% CI, 4.4 to 8.3]; ACT: 4.5 [95% CI, 2.8 to 6.1]). During treatment, there were some clinically meaningful differences between groups for other symptoms but not for function subscales or global health status.
Conclusion: Treatment-emergent symptoms from OL were limited, generally resolving after treatment ended. OL- and PL-treated patients had similar functional scores, slowly improving during the 24 months after (N)ACT and there was no clinically meaningful persistence of fatigue severity in OL-treated patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02032823.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Is adjuvant olaparib standard of care in all high-risk HER2-negative early breast cancer presenting gBRCA1/2 mutations?Gland Surg. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):257-262. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-467. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Gland Surg. 2025. PMID: 40115853 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bower JE, Ganz PA, Desmond KA, et al. Fatigue in breast cancer survivors: Occurrence, correlates, and impact on quality of life. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:743–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

