T helper cells exhibit a dynamic and reversible 3'-UTR landscape
- PMID: 38302256
- PMCID: PMC10946431
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.079897.123
T helper cells exhibit a dynamic and reversible 3'-UTR landscape
Abstract
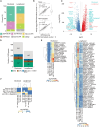
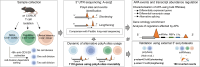
3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs) are critical elements of messenger RNAs, as they contain binding sites for RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNAs that affect various aspects of the RNA life cycle including transcript stability and cellular localization. In response to T cell receptor activation, T cells undergo massive expansion during the effector phase of the immune response and dynamically modify their 3' UTRs. Whether this serves to directly regulate the abundance of specific mRNAs or is a secondary effect of proliferation remains unclear. To study 3'-UTR dynamics in T helper cells, we investigated division-dependent alternative polyadenylation (APA). In addition, we generated 3' end UTR sequencing data from naive, activated, memory, and regulatory CD4+ T cells. 3'-UTR length changes were estimated using a nonnegative matrix factorization approach and were compared with those inferred from long-read PacBio sequencing. We found that APA events were transient and reverted after effector phase expansion. Using an orthogonal bulk RNA-seq data set, we did not find evidence of APA association with differential gene expression or transcript usage, indicating that APA has only a marginal effect on transcript abundance. 3'-UTR sequence analysis revealed conserved binding sites for T cell-relevant microRNAs and RBPs in the alternative 3' UTRs. These results indicate that poly(A) site usage could play an important role in the control of cell fate decisions and homeostasis.
Keywords: 3′-UTR usage; T helper cells; alternative polyadenylation; effector/memory T cells; naive T cells; posttranscriptional regulation; proliferation.
© 2024 Seyres et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
