Long-term intermittent hypoxia in mice induces inflammatory pathways implicated in sleep apnea and steatohepatitis in humans
- PMID: 38303705
- PMCID: PMC10830848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108837
Long-term intermittent hypoxia in mice induces inflammatory pathways implicated in sleep apnea and steatohepatitis in humans
Abstract
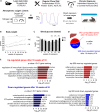
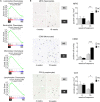
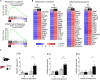
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) induces intermittent hypoxia (IH), an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). While the molecular links between IH and NAFLD progression are unclear, immune cell-driven inflammation plays a crucial role in NAFLD pathogenesis. Using lean mice exposed to long-term IH and a cohort of lean OSA patients (n = 71), we conducted comprehensive hepatic transcriptomics, lipidomics, and targeted serum proteomics. Significantly, we demonstrated that long-term IH alone can induce NASH molecular signatures found in human steatohepatitis transcriptomic data. Biomarkers (PPARs, NRFs, arachidonic acid, IL16, IL20, IFNB, TNF-α) associated with early hepatic and systemic inflammation were identified. This molecular link between IH, sleep apnea, and steatohepatitis merits further exploration in clinical trials, advocating for integrating sleep apnea diagnosis in liver disease phenotyping. Our unique signatures offer potential diagnostic and treatment response markers, highlighting therapeutic targets in the comorbidity of NAFLD and OSA.
Keywords: Animal physiology; Biological sciences; Human Physiology; Natural sciences; Physiology.
© 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Lévy P., Kohler M., McNicholas W.T., Barbé F., McEvoy R.D., Somers V.K., Lavie L., Pépin J.L. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2015;1 - PubMed
-
- Jullian-Desayes I., Trzepizur W., Boursier J., Joyeux-Faure M., Bailly S., Benmerad M., Le Vaillant M., Jaffre S., Pigeanne T., Bizieux-Thaminy A., et al. Obstructive sleep apnea, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and NAFLD: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2021;77:357–364. - PubMed
-
- Aron-Wisnewsky J., Minville C., Tordjman J., Lévy P., Bouillot J.-L., Basdevant A., Bedossa P., Clément K., Pépin J.L. Chronic intermittent hypoxia is a major trigger for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in morbid obese. J. Hepatol. 2012;56:225–233. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

