Development and application of an amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay for the accurate quantification of kidney injury molecule-1
- PMID: 38304229
- PMCID: PMC10832993
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1280681
Development and application of an amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay for the accurate quantification of kidney injury molecule-1
Abstract
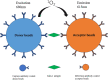
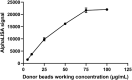
Background: Kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1), a specific marker of kidney injury, is usually not expressed in normal kidneys or at very low levels but is highly expressed in injured renal tubular epithelial cells until the damaged cells recover completely. Therefore, we aimed to develop an efficient and highly sensitive assay to accurately quantify Kim-1 levels in human serum and urine. Methods: In this study, a novel immunoassay was developed and named amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay (AlphaLISA). Anti-Kim-1 antibodies can be directly coupled to carboxyl-modified donor and acceptor beads for the rapid detection of Kim-1 by double-antibody sandwich method. Serum and urine samples for Kim-1 measurements were obtained from 129 patients with nephropathy and 17 healthy individuals. Results: The linear range of Kim-1 detected by AlphaLISA was 3.83-5000 pg/mL, the coefficients of variation of intra-assay and inter-assay batches were 3.36%-4.71% and 5.61%-11.84%, respectively, and the recovery rate was 92.31%-99.58%. No cross reactions with neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, liver-type fatty acid binding protein, and matrix metalloproteinase-3 were observed. A good correlation (R 2 = 0.9086) was found between the findings of Kim-1-TRFIA and Kim-AlphaLISA for the same set of samples. In clinical trials, both serum and urine Kim-1 levels were significantly higher in patients with nephropathy than in healthy individuals, especially in patients with acute kidney injury. Furthermore, serum Kim-1 was superior to urinary Kim-1 in distinguishing between patients with nephropathy and healthy individuals. Conclusion: The developed Kim-1-AlphaLISA is highly efficient, precise, and sensitive, and it is suitable for the rapid detection of patients with acute kidney injury.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay linked immunosorbent assay; double-antibody sandwich; kidney injury molecule-1; serum; urine.
Copyright © 2024 Fu, Sun, Qin, Zheng, Zhou, Zhou, Zhao, Xu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




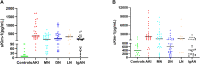
Similar articles
-
Sensitive amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay for the quantitative detection of CA242.J Immunol Methods. 2023 Jun;517:113487. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2023.113487. Epub 2023 May 6. J Immunol Methods. 2023. PMID: 37156407
-
Establishment of a time-resolved immunoassay for acute kidney injury based on the detection of Kim-1.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Sep;36(9):e24603. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24603. Epub 2022 Jul 23. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35870181 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury in an obstructive nephropathy patient.Nephrology (Carlton). 2014 Apr;19(4):186-94. doi: 10.1111/nep.12173. Nephrology (Carlton). 2014. PMID: 24165570
-
Earlier recognition of nephrotoxicity using novel biomarkers of acute kidney injury.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011 Oct;49(8):720-8. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2011.615319. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011. PMID: 21970770 Review.
-
Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 in renal disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2018 Dec;487:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Clin Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 30201372 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

