Functional dysconnectivity and microstructural impairment of the cortico-thalamo-cortical network in women with rheumatoid arthritis: A multimodal MRI study
- PMID: 38304809
- PMCID: PMC10830510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24725
Functional dysconnectivity and microstructural impairment of the cortico-thalamo-cortical network in women with rheumatoid arthritis: A multimodal MRI study
Abstract
Background: Cognitive deficits are common in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, but the mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated the effective connectivity and structural alterations of the core brain regions in RA patients with cognitive impairment.
Methods: Twenty-four female patients with RA and twenty-four healthy controls were enrolled. We analyzed abnormal brain activity patterns using functional MRI during the Iowa gambling task (IGT) and core regions effective connectivity using dynamic causal model (DCM). Structural alterations of white matter volume (WMV) and gray matter volume (GMV) were detected using voxel-based morphometry (VBM).
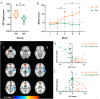
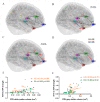
Results: RA patients showed altered activation patterns of the cortico-thalamo-cortical network, increased coupling strength from the left ventromedial prefrontal gyrus to the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), the ACC to the right thalamus, and decreased connectivity from the thalamus to left hippocampus. VBM structural analysis showed increased GMV in the bilateral orbital frontal gyrus, bilateral hippocampus and right putamen, and reduced GMV and WMV in the bilateral thalamus in RA patients. Right thalamic GMV and WMV were positively correlated with the right thalamus-to-hippocampus connective strength. Additionally, the bold signal, GMV and WMV of the right thalamus were positively correlated with cognitive performance (IGT score) in RA patients.
Conclusion: Results suggest a structural and functional deficiency in the cortico-thalamo-cortical network, which is characterized by increased ACC-to-thalamus strength and reduced thalamus-to-hippocampus coupling in RA patients. The cognitive dysfunction may be the result of compensatory measures against imbalanced cortico-thalamic-cortical coupling.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Cortico-thalamo-cortical network; DCM; Rheumatoid arthritis; VBM.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fronto-thalamic structural and effective connectivity and delusions in schizophrenia: a combined DTI/DCM study.Psychol Med. 2021 Sep;51(12):2083-2093. doi: 10.1017/S0033291720000859. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Psychol Med. 2021. PMID: 32329710 Free PMC article.
-
Common and distinct abnormal frontal-limbic system structural and functional patterns in patients with major depression and bipolar disorder.Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Jul 6;20:42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.07.002. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30069426 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased grey matter volume in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and thalamus accompanied by compensatory increases in middle cingulate gyrus of premature ejaculation patients.Andrology. 2024 May;12(4):841-849. doi: 10.1111/andr.13547. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Andrology. 2024. PMID: 37902180
-
Gray Matter Atrophy in the Cortico-Striatal-Thalamic Network and Sensorimotor Network in Relapsing-Remitting and Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis.Neuropsychol Rev. 2021 Dec;31(4):703-720. doi: 10.1007/s11065-021-09479-3. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Neuropsychol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33582965 Review.
-
A multimodal meta-analysis of regional functional and structural brain abnormalities in obsessive-compulsive disorder.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Feb;274(1):165-180. doi: 10.1007/s00406-023-01594-x. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37000246
References
-
- Jeffery R.C. Clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine. 2014;42:231–236.
-
- Wallin K., Solomon A., Kåreholt I., Tuomilehto J., Soininen H., Kivipelto M. Midlife rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of cognitive impairment two decades later: a population-based study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;31:669–676. - PubMed
-
- Vitturi B.K., Nascimento B.A.C., Alves B.R., de Campos F.S.C., Torigoe D.Y. Cognitive impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019;69:81–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

